Study indicates widespread SARS-CoV-2 exposure in wildlife SARSCoV2 Coronavirus Disease COVID Zoonosis Virginia Opossum Deer Raccoons Squirrels biorxivpreprint virginia_tech
SARS-CoV-2 spillover onto humans has led to the devastating COVID-19 pandemic that has caused significant morbidity and mortality across the globe. Interactions of humans with animals have caused the reverse transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from humans to captive and wild animal species.
Eighteen wild animal species and 333 individuals from 32 counties of Virginia were sampled in the Eastern regions of the United States and subjected to RT-qPCR and WGS analyses. Nasopharyngeal swabs were obtained for detecting the SARS-CoV-2 spike , nucleocapsid , and envelope genes and for amplifying a housekeeping-type gene to assess the prevalence of active COVID-19 cases.
Results The team detected widespread SARS-CoV-2 exposure among wildlife. SARS-CoV-2 was identified in Virginia’s opossum and equivocally among six other species. Raccoons and squirrels showed high SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence ranging between 62% and 71%, and the seroprevalence was three times higher among high human-activity areas than low human-activity areas.
The sequence of SARS-CoV-2 obtained from the infected Virginia opossum shared mutations in the Omicron BA.2 open reading frame 1a/b , membrane , E, and S genes. The detected isolate was found to cluster in the Omicron clade and was assigned the Omicron sub-variant BJ.1 or BA.2.10.1. The BA.2.10.1 subvariant comprised the G798D amino acid substitution in the S protein.
Brasil Últimas Notícias, Brasil Manchetes
Similar News:Você também pode ler notícias semelhantes a esta que coletamos de outras fontes de notícias.
 SARS-CoV-2 activates NLRP3 inflammasomeResearchers assessed the role of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in the NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation.
SARS-CoV-2 activates NLRP3 inflammasomeResearchers assessed the role of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in the NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation.
Consulte Mais informação »
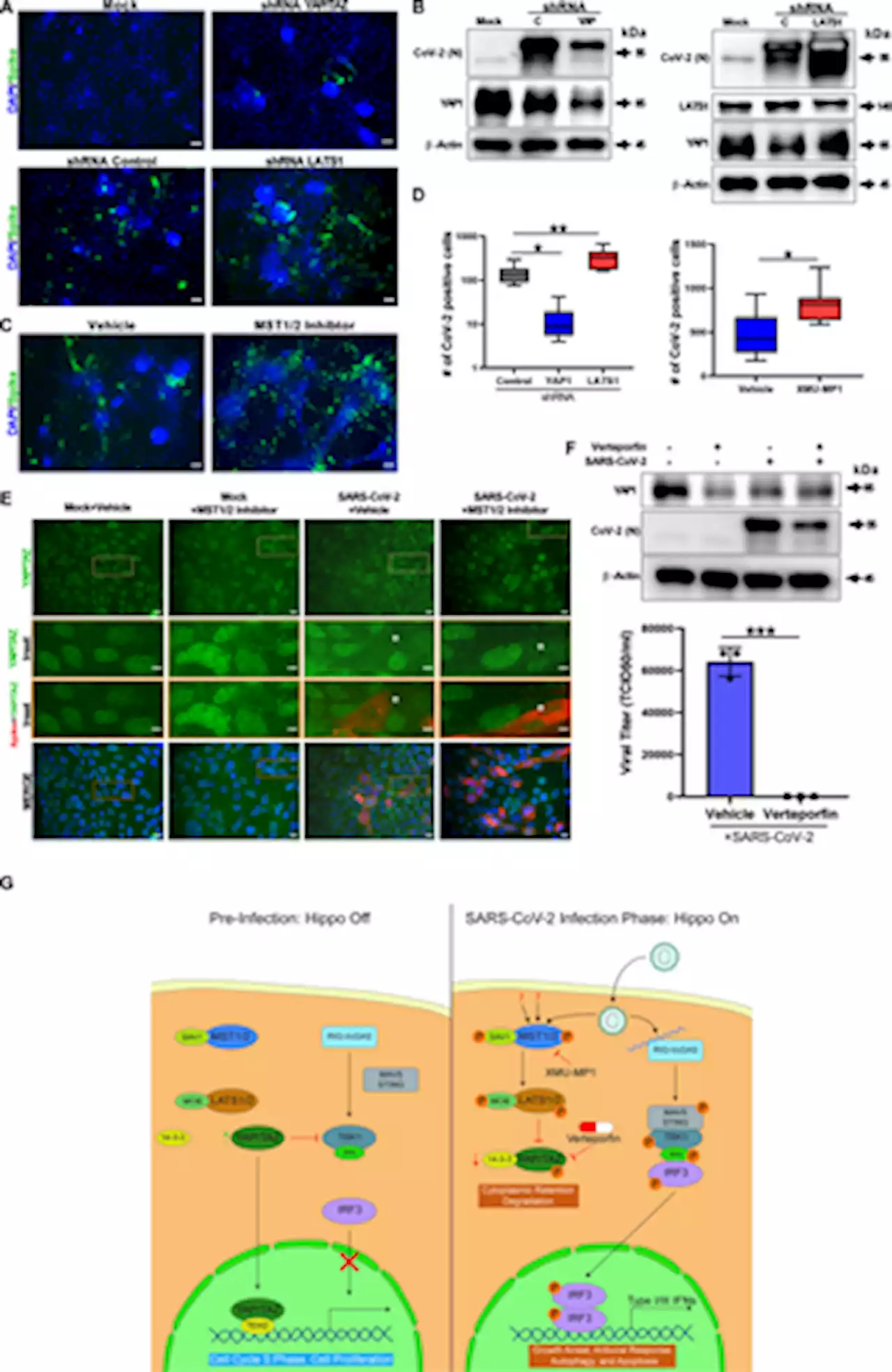 Hippo signaling pathway activation during SARS-CoV-2 infection contributes to host antiviral responseThis study shows that SARS-CoV-2 infection leads to activation of the Hippo signaling pathway in human COVID-19 lung tissue and cultured cells. The Hippo signaling pathway appears to play an antiviral role, and pharmacological inhibition of the downstream transactivator YAP reduces SARS-CoV-2 replication, with therapeutic implications.
Hippo signaling pathway activation during SARS-CoV-2 infection contributes to host antiviral responseThis study shows that SARS-CoV-2 infection leads to activation of the Hippo signaling pathway in human COVID-19 lung tissue and cultured cells. The Hippo signaling pathway appears to play an antiviral role, and pharmacological inhibition of the downstream transactivator YAP reduces SARS-CoV-2 replication, with therapeutic implications.
Consulte Mais informação »
 Hybrid immunity from vaccination and Omicron BA.1 or BA.5 breakthrough infections exhibits cross-reactive efficacy against BA.2.75Researchers recently measured the neutralizing antibody titers against the wild-type strain of SARS-CoV-2 and the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants in healthcare workers fully vaccinated with three doses of the Comirnaty vaccine who experienced breakthrough Omicron infections.
Hybrid immunity from vaccination and Omicron BA.1 or BA.5 breakthrough infections exhibits cross-reactive efficacy against BA.2.75Researchers recently measured the neutralizing antibody titers against the wild-type strain of SARS-CoV-2 and the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants in healthcare workers fully vaccinated with three doses of the Comirnaty vaccine who experienced breakthrough Omicron infections.
Consulte Mais informação »
 SARS-CoV-2 Nsp6 damages Drosophila heart and mouse cardiomyocytes through MGA/MAX complex-mediated increased glycolysis - Communications BiologySARS-CoV-2 protein expression studies in the Drosophila heart suggest a cause of COVID-19-associated cardiac pathology via interaction of virus Nsp6 with the host MGA/MAX complex disrupting glycolysis and cardiac mitochondrial function.
SARS-CoV-2 Nsp6 damages Drosophila heart and mouse cardiomyocytes through MGA/MAX complex-mediated increased glycolysis - Communications BiologySARS-CoV-2 protein expression studies in the Drosophila heart suggest a cause of COVID-19-associated cardiac pathology via interaction of virus Nsp6 with the host MGA/MAX complex disrupting glycolysis and cardiac mitochondrial function.
Consulte Mais informação »
 Does the time of day patients receive their COVID-19 vaccinations influence their clinical benefit?Does the time of day patients receive their COVID-19 vaccinations influence their clinical benefit? medrxivpreprint WUSTLmed YaleMed COVID19 coronavirus covid vaccinations vaccine vaccination SARSCoV2
Does the time of day patients receive their COVID-19 vaccinations influence their clinical benefit?Does the time of day patients receive their COVID-19 vaccinations influence their clinical benefit? medrxivpreprint WUSTLmed YaleMed COVID19 coronavirus covid vaccinations vaccine vaccination SARSCoV2
Consulte Mais informação »
 Paxlovid antiviral therapy reduces risk of long COVIDIn a recent study posted to the medRxiv* server, researchers in Saint Louis, Missouri, examined whether nirmatrelvir treatment reduced the risk of long COVID, the disease encompassing the post-acute sequelae of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) [PASC].
Paxlovid antiviral therapy reduces risk of long COVIDIn a recent study posted to the medRxiv* server, researchers in Saint Louis, Missouri, examined whether nirmatrelvir treatment reduced the risk of long COVID, the disease encompassing the post-acute sequelae of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) [PASC].
Consulte Mais informação »
