Key mechanisms to improve intestinal regeneration and alleviate the side effects of radiotherapy discovered CNIO_Cancer JExpMed
Intestinal epithelium regenerates rapidly through proliferation of intestinal stem cells , orchestrated by potent mitogens secreted within the crypt niche. However, mechanisms regulating these mitogenic factors remain largely unknown. Here, we demonstrate that transit-amplifying cells, marked by unconventional prefoldin RPB5 interactor , control R-spondin production to guide ISC proliferation.
R-spondin supplementation or restoration of R-spondin levels via cell death inhibition by c-MYC elimination or the suppression of inflammation reinstates ISC proliferation in URI-depleted mice. However, selective c-MYC and p53 suppression are required to fully restore TA cell survival and differentiation capacity and preserve complete intestinal architecture.
Brasil Últimas Notícias, Brasil Manchetes
Similar News:Você também pode ler notícias semelhantes a esta que coletamos de outras fontes de notícias.
 ‘Light at end of tunnel’ as man finishes gruelling Mexico chemo to halt MSScott McPhillimy, 34, is being treated at Clinica Ruiz in Puebla for a haematopoietic stem cell transplantation to stop his young wife going into…
‘Light at end of tunnel’ as man finishes gruelling Mexico chemo to halt MSScott McPhillimy, 34, is being treated at Clinica Ruiz in Puebla for a haematopoietic stem cell transplantation to stop his young wife going into…
Consulte Mais informação »
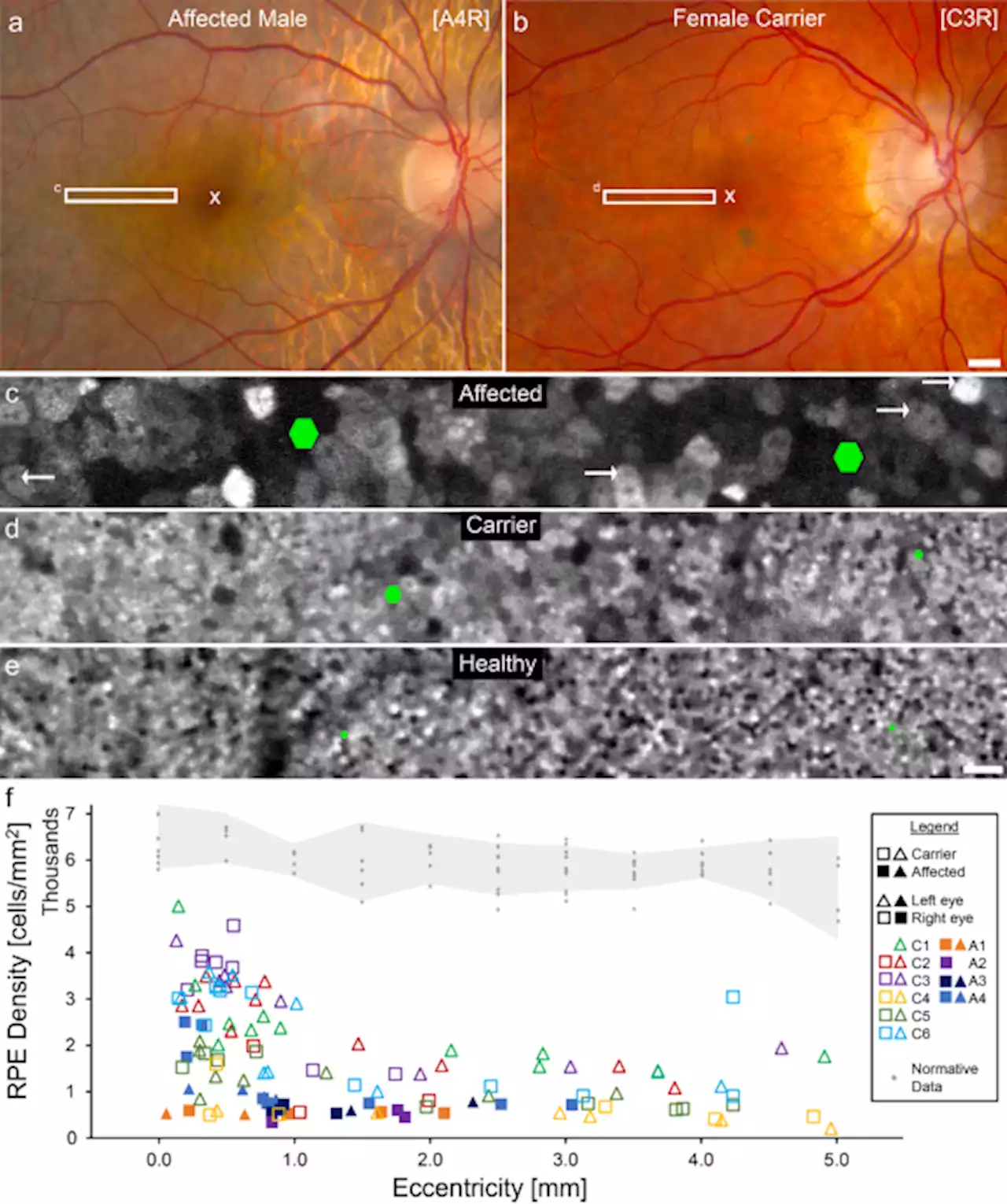 Widespread subclinical cellular changes revealed across a neural-epithelial-vascular complex in choroideremia using adaptive optics - Communications BiologyThe in vivo pathogenesis of the blinding retinal degeneration choroideremia is visualized, which reveals enlarged and area-disrupted retinal pigment epithelial cells, providing evidence for polymegathism in choroideremia.
Widespread subclinical cellular changes revealed across a neural-epithelial-vascular complex in choroideremia using adaptive optics - Communications BiologyThe in vivo pathogenesis of the blinding retinal degeneration choroideremia is visualized, which reveals enlarged and area-disrupted retinal pigment epithelial cells, providing evidence for polymegathism in choroideremia.
Consulte Mais informação »
 Warning issued to vapers as scientists suggest it may 'wake up' cancer cellsMedical experts say that the dangers of vaping are still not fully known.
Warning issued to vapers as scientists suggest it may 'wake up' cancer cellsMedical experts say that the dangers of vaping are still not fully known.
Consulte Mais informação »
 Mucosal vaccination triggers superior T cell response against SARS-CoV-2 variantsIn a recent study posted to the bioRxiv* server, researchers in Singapore and the United States demonstrated that intranasal (I.N.) delivery of a mucosal severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccination triggered a superior T cell response compared to an equivalent dose of antigen delivered by the subcutaneous (S.C.) route.
Mucosal vaccination triggers superior T cell response against SARS-CoV-2 variantsIn a recent study posted to the bioRxiv* server, researchers in Singapore and the United States demonstrated that intranasal (I.N.) delivery of a mucosal severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccination triggered a superior T cell response compared to an equivalent dose of antigen delivered by the subcutaneous (S.C.) route.
Consulte Mais informação »
 Altered T-cell response in hemodialysis patients following third COVID-19 vaccine doseAltered T-cell response in hemodialysis patients following third COVID-19 vaccine dose Cell Coronavirus Disease COVID TCell Vaccine hemodialysis biorxivpreprint UMontreal mcgillu
Altered T-cell response in hemodialysis patients following third COVID-19 vaccine doseAltered T-cell response in hemodialysis patients following third COVID-19 vaccine dose Cell Coronavirus Disease COVID TCell Vaccine hemodialysis biorxivpreprint UMontreal mcgillu
Consulte Mais informação »