Earth may have been exposed to more UV in the past than thought. That radiation is deadly to life, but also may have spurred evolution on.
Fortunately for us, the Earth’s layer provides varying levels of UV protection across the Earth’s surface which varies with season and latitude. Overall, it prevents between 97% and 99% of the Sun’s medium-frequency UV light from striking the Earth’s surface. But the ozone layer’s effectiveness is dependent on the oxygen content in Earth’s atmosphere, and that content has fluctuated over time.
Earth’s oxygen level has fluctuated over time, but the GOE is the most significant event in the history of Earth’s oxygen levels. Another event named the Neoproterozoic Oxygenation Event may have also played an essential role in raising Earth’s oxygen levels. Still, it’s not as well-understood—or even agreed-upon—as the GOE. But in any case, as oxygen levels go, so goes the ozone.
Models of Earth’s climate history are the basis of this study. The models show that previous estimates of surface UV levels could have underestimated UV exposure. Instead, Earth might have been subjected to ten times more UV than we thought. This image is a schematic of the WACCM6 Earth System Model. In this work, WACCM6 used a fully interactive ocean model and land-ice, sea-ice, land and atmosphere models. WACCM6 has fully coupled chemistry and physics, a state-of-the-art moist physics scheme, and simulates up to roughly 140 km in altitude in the pre-industrial atmosphere. Image Credit: Cooke et al. 2022/University of Leedsto measure atmospheric ozone levels.
“If our modelling is indicative of atmospheric scenarios during Earth’s oxygenated history, then for over a billion years, the Earth could have been bathed in UV radiation that was much more intense than previously believed,” Cooke said.
Brasil Últimas Notícias, Brasil Manchetes
Similar News:Você também pode ler notícias semelhantes a esta que coletamos de outras fontes de notícias.
 Here's What Would Really Happen if Earth Had an Impact EventNo impact crater was ever found from the Tunguska event because the meteorite is believed to have disintegrated at an altitude of 5 to 10 kilometers (3 to 6 miles).
Here's What Would Really Happen if Earth Had an Impact EventNo impact crater was ever found from the Tunguska event because the meteorite is believed to have disintegrated at an altitude of 5 to 10 kilometers (3 to 6 miles).
Consulte Mais informação »
 We May Have Seriously Underestimated How Hostile Conditions on Early Earth WereScientists have been doing some great work when it comes to peering back through billions of years to figure out what ancient Earth would have looked like, and a new study reveals that the earliest conditions on our planet were probably even more hos
We May Have Seriously Underestimated How Hostile Conditions on Early Earth WereScientists have been doing some great work when it comes to peering back through billions of years to figure out what ancient Earth would have looked like, and a new study reveals that the earliest conditions on our planet were probably even more hos
Consulte Mais informação »
 After the dinosaurs, Earth became an all-you-can-eat buffet for snakesEarly snakes slithered into newly vacant ecological niches and rapidly evolved the ability to go after a wide array of prey.
After the dinosaurs, Earth became an all-you-can-eat buffet for snakesEarly snakes slithered into newly vacant ecological niches and rapidly evolved the ability to go after a wide array of prey.
Consulte Mais informação »
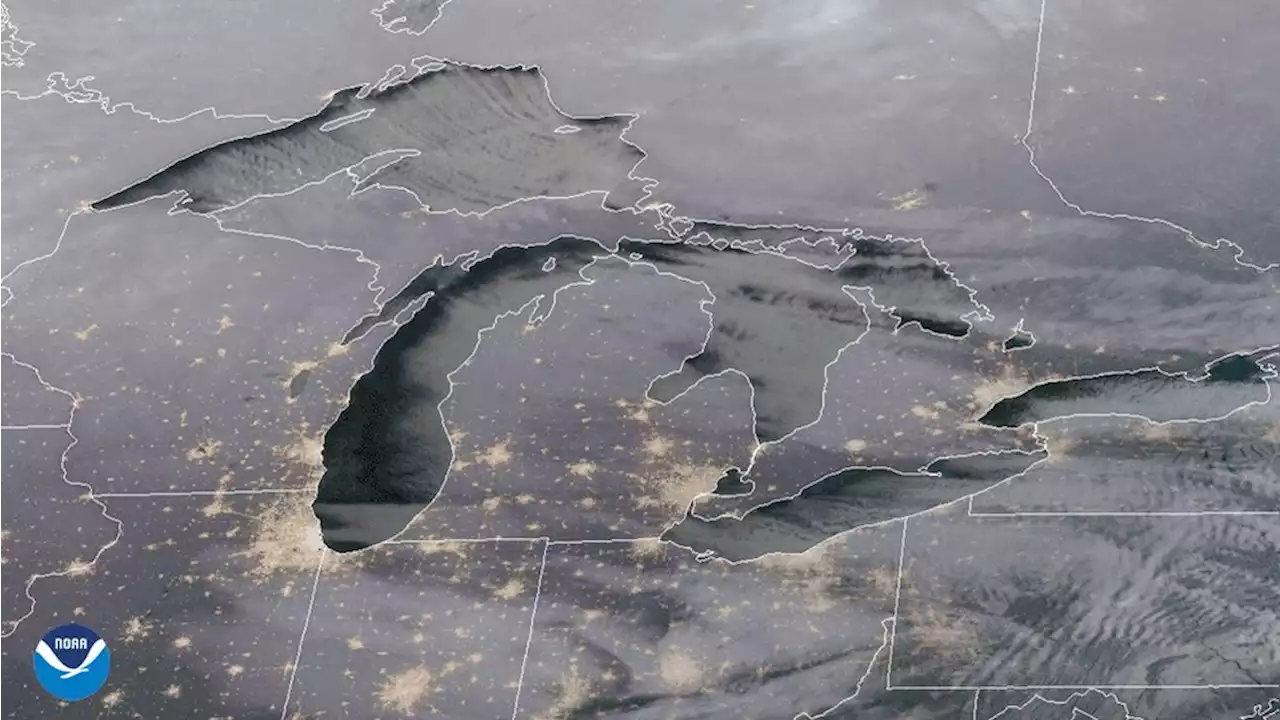 Earth from Orbit: Superior Flow of CloudsGOESEast captured this spectacular view of Lake Effect clouds streaming over the Great Lakes as the sun rose this morning over the region. This phenomenon is dumping heavy snow downwind of the lakes. Learn more in this previous EarthFromOrbit video:
Earth from Orbit: Superior Flow of CloudsGOESEast captured this spectacular view of Lake Effect clouds streaming over the Great Lakes as the sun rose this morning over the region. This phenomenon is dumping heavy snow downwind of the lakes. Learn more in this previous EarthFromOrbit video:
Consulte Mais informação »
 This Eerie Similarity With Earth Has Finally Solved The Mystery of Jupiter's CyclonesEarth and Jupiter don't have a lot in common.
This Eerie Similarity With Earth Has Finally Solved The Mystery of Jupiter's CyclonesEarth and Jupiter don't have a lot in common.
Consulte Mais informação »
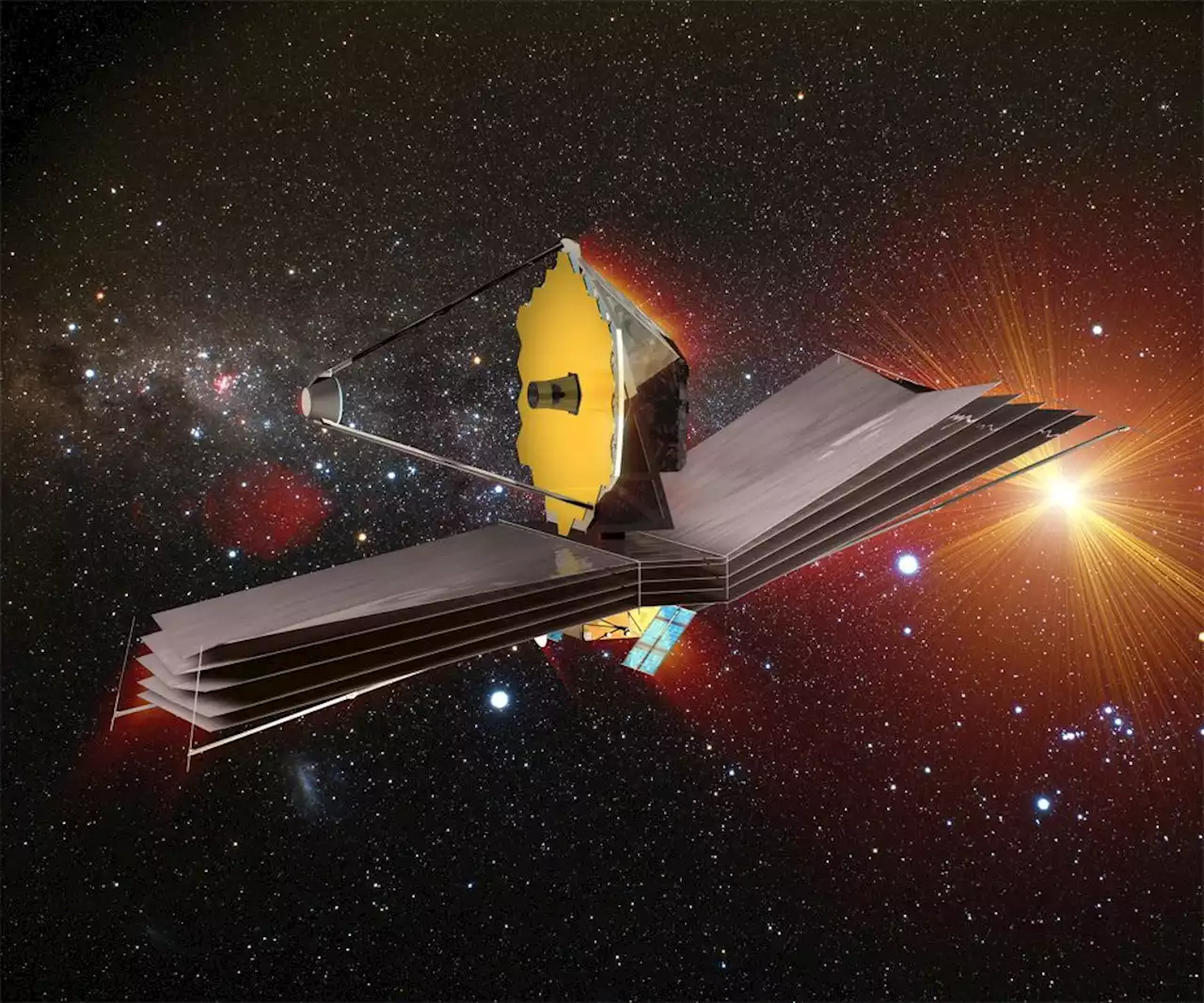 The James Webb Space Telescope is fully deployed. So what's next for the biggest observatory off Earth?The generational observatory is en route to its parking spot and getting ready to test its mirrors and instruments.
The James Webb Space Telescope is fully deployed. So what's next for the biggest observatory off Earth?The generational observatory is en route to its parking spot and getting ready to test its mirrors and instruments.
Consulte Mais informação »
