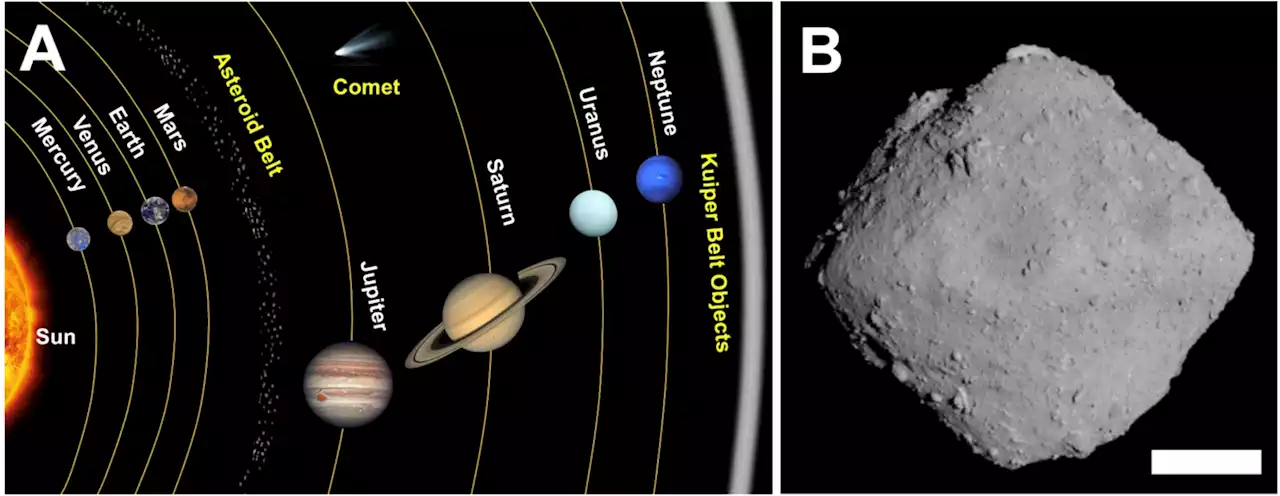
Japan's Aerospace Exploration Agency sent the Hayabusa2 spacecraft to 162173 Ryugu in 2019, an asteroid in orbit near Earth that is comprised of rocky fragments originating from a larger parent body. Multiple rovers brought samples from the asteroid's surface back down to Earth for scientists to study.
C-rich compounds are preferentially released , 2) fractional crystallization where the formation of early carbonates changes the composition of the remaining reservoir from which subsequent carbonates can crystallize, 3) mixing of multiple carbon reservoirs with differentC ratios, and 4) varying oxygen and hydrogen caused changes in the isotopes forming carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and methane, from which carbon is obtained for the crystals.
Similarly, fractional crystallization is ruled out, as is mixing ofTherefore, it is the latter scenario of varying oxygen that is suggested as the main driver of changes inC ratios. This resulted from the oxidation of iron in the rock by water and is measured based upon the production of hydrogen released from the water. The hypothesis matches observations of increasing iron in the meteorite with progressive alteration.
Brasil Últimas Notícias, Brasil Manchetes
Similar News:Você também pode ler notícias semelhantes a esta que coletamos de outras fontes de notícias.
 Beaming Solar Energy From Space to Earth Could Soon Be a RealityThe idea of space-based solar power (SBSP) – using satellites to collect energy from the Sun and 'beam' it to collection points on Earth – has been around since at least the late 1960s.
Beaming Solar Energy From Space to Earth Could Soon Be a RealityThe idea of space-based solar power (SBSP) – using satellites to collect energy from the Sun and 'beam' it to collection points on Earth – has been around since at least the late 1960s.
Consulte Mais informação »
 The largest asteroid impact crater on Earth is lurking beneath Australia, new evidence suggestsGeophysical evidence suggests there is a massive, magnetized structure deep beneath Australia. Experts think it could be the remnants of the largest meteor crater on Earth.
The largest asteroid impact crater on Earth is lurking beneath Australia, new evidence suggestsGeophysical evidence suggests there is a massive, magnetized structure deep beneath Australia. Experts think it could be the remnants of the largest meteor crater on Earth.
Consulte Mais informação »
 Irrigation benefits outweigh costs in more US croplands by mid-century - Communications Earth & EnvironmentBenefit to cost ratio of crop irrigation is projected to increase by mid-century in the north-central US and upper mid-West for maize and central US for soybean, suggests an analysis of future climate scenarios.
Irrigation benefits outweigh costs in more US croplands by mid-century - Communications Earth & EnvironmentBenefit to cost ratio of crop irrigation is projected to increase by mid-century in the north-central US and upper mid-West for maize and central US for soybean, suggests an analysis of future climate scenarios.
Consulte Mais informação »
 San Jose cat’s perplexing habits: scratching around her food dish and hanging out under the bedAnd what on earth is that hawk doing with that sparrow?
San Jose cat’s perplexing habits: scratching around her food dish and hanging out under the bedAnd what on earth is that hawk doing with that sparrow?
Consulte Mais informação »
 Record shattering: Earth had its hottest July in 174 years(5 of 5) SEE our Significant Climate Events Map. The globe saw 8 named storms in July — 3 of which reached major tropical cyclone strength. See more: NOAANCEI StateOfClimate
Record shattering: Earth had its hottest July in 174 years(5 of 5) SEE our Significant Climate Events Map. The globe saw 8 named storms in July — 3 of which reached major tropical cyclone strength. See more: NOAANCEI StateOfClimate
Consulte Mais informação »