A study published in BMCGeriatr finds that community-dwellers with Alzheimer’s disease have a higher incidence of pneumonia than community-dwellers without the disease.
). In addition, the use of benzodiazepines and related drugs and antipsychotics, as well as antiepileptics, opioids, oral glucocorticoids, and proton pump inhibitors, was more common in this group.Full size tableOut of all the investigated risk factors, previous hospital-treated pneumonia had the strongest association with incident pneumonia in the whole population with incident pneumonia . Male gender , AD , all comorbidities and drug use were associated with incident pneumonia.
When risk factor analyses were performed separately in the AD and non-AD cohorts, previous pneumonia was a strong risk factor for pneumonia in both cohorts . Except for antidepressants, biological products, benzodiazepines or related drugs, and liver or kidney disease that had no association with pneumonia in the AD cohort, all comorbidities, and drug use were associated with the increased risk of pneumonia in both cohorts. The associations were stronger in the non-AD cohort.
In the competing risk models, in persons with AD cardiovascular diseases, liver and kidney disease, oral glucocorticoids, and biological products were not associated with pneumonia. In persons without AD, the associations of liver and kidney disease and biological products were no longer associated with increased risk of pneumonia in the competing risk models.In this study, the AD cohort had a higher incidence of pneumonia than the non-AD cohort.
A previous study on the incidence of bacterial pneumonia showed a higher risk of hospitalization for persons with cognitive impairment []. Our findings are similar; however, we included a broader range of pneumonia diagnoses including viral pneumonia caused by for example influenza virus and other common respiratory viruses. This implies that the risk is higher in persons with AD not only for bacterial pneumonia but also for viral pneumonia.
Although the same risk factors were associated with a higher risk of pneumonia in both cohorts, nearly all risk factors had stronger associations in the AD cohort. This is consistent with our earlier studies on risk factors of hip fracture [
Brasil Últimas Notícias, Brasil Manchetes
Similar News:Você também pode ler notícias semelhantes a esta que coletamos de outras fontes de notícias.
 Rates of maternal weight gain over the course of pregnancy and offspring risk of neurodevelopmental disorders - BMC MedicineBackground Previous studies have suggested that gestational weight gain (GWG) outside an optimal range increases the risks of neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs) in offspring including autism spectrum disorder (ASD), intellectual disability (ID), and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The sequential development of the fetal brain suggests that its vulnerability may vary depending on the timing of exposure. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the associations of not only gestational age-standardized total GWG (GWG z-scores) but also the rate of GWG (RGWG) in the second and third trimesters with risks of NDDs in offspring. Methods In this population-based cohort study, we used maternal weight data from antenatal care records collected for 57,822 children born to 53,516 mothers between 2007 and 2010 in the Stockholm Youth Cohort. Children were followed from 2 years of age to December 31, 2016. GWG z-scores and RGWG (kg/week) in the second and third trimesters were considered as continuous variables in cox regression models, clustered on maternal identification numbers. Nonlinear relationships were accommodated using restricted cubic splines with 3 knots. RGWG were also categorized according to the 2009 US Institute of Medicine (IOM) guidelines for optimal GWG. According to the IOM guidelines, the optimal rate of GWG for the second and third trimesters for underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obese categories were 0.44–0.58, 0.35–0.50, 0.23–0.33, and 0.17–0.27 kg/week, respectively. Results During a mean follow-up of 5.4 years (until children were on average 7.4 years old), 2205 (3.8%) children were diagnosed with NDDs, of which 1119 (1.9%) received a diagnosis of ASD, 1353 (2.3%) ADHD, and 270 (0.5%) ID. We observed a J-shaped association between total GWG z-score and offspring risk of NDDs, with higher total GWG (GWG z-score=2) associated with 19% increased risk of any NDD (95% CI=3–37%) and lower total GWG (GWG z-score=− 2) associated with 12% inc
Rates of maternal weight gain over the course of pregnancy and offspring risk of neurodevelopmental disorders - BMC MedicineBackground Previous studies have suggested that gestational weight gain (GWG) outside an optimal range increases the risks of neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs) in offspring including autism spectrum disorder (ASD), intellectual disability (ID), and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The sequential development of the fetal brain suggests that its vulnerability may vary depending on the timing of exposure. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the associations of not only gestational age-standardized total GWG (GWG z-scores) but also the rate of GWG (RGWG) in the second and third trimesters with risks of NDDs in offspring. Methods In this population-based cohort study, we used maternal weight data from antenatal care records collected for 57,822 children born to 53,516 mothers between 2007 and 2010 in the Stockholm Youth Cohort. Children were followed from 2 years of age to December 31, 2016. GWG z-scores and RGWG (kg/week) in the second and third trimesters were considered as continuous variables in cox regression models, clustered on maternal identification numbers. Nonlinear relationships were accommodated using restricted cubic splines with 3 knots. RGWG were also categorized according to the 2009 US Institute of Medicine (IOM) guidelines for optimal GWG. According to the IOM guidelines, the optimal rate of GWG for the second and third trimesters for underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obese categories were 0.44–0.58, 0.35–0.50, 0.23–0.33, and 0.17–0.27 kg/week, respectively. Results During a mean follow-up of 5.4 years (until children were on average 7.4 years old), 2205 (3.8%) children were diagnosed with NDDs, of which 1119 (1.9%) received a diagnosis of ASD, 1353 (2.3%) ADHD, and 270 (0.5%) ID. We observed a J-shaped association between total GWG z-score and offspring risk of NDDs, with higher total GWG (GWG z-score=2) associated with 19% increased risk of any NDD (95% CI=3–37%) and lower total GWG (GWG z-score=− 2) associated with 12% inc
Consulte Mais informação »
 Japanese study finds Cesarean births increase childhood obesity riskJapanese study finds Cesarean births increase childhood obesity risk CesareanSection ChildhoodObesity Japanese Children BirthCohortStudy ObesityRisk HealthImpact Japan Research PublicHealth MaternalHealth SciReports
Japanese study finds Cesarean births increase childhood obesity riskJapanese study finds Cesarean births increase childhood obesity risk CesareanSection ChildhoodObesity Japanese Children BirthCohortStudy ObesityRisk HealthImpact Japan Research PublicHealth MaternalHealth SciReports
Consulte Mais informação »
 Charles II Coronation etchings found in cupboardThe images, which are more than 350 years old, were found during a house clearance in Notting Hill
Charles II Coronation etchings found in cupboardThe images, which are more than 350 years old, were found during a house clearance in Notting Hill
Consulte Mais informação »
 Charles II Coronation etchings found in cupboardWhat a find! The 20 images, created in 1661, illustrate the restored Stuart king's procession to Westminster Abbey.
Charles II Coronation etchings found in cupboardWhat a find! The 20 images, created in 1661, illustrate the restored Stuart king's procession to Westminster Abbey.
Consulte Mais informação »
 Prezzo to shut 46 restaurants putting 810 staff at risk - full list of sites closingThe move will put around 810 workers at risk of redundancy, the Italian restaurant chain said, although it will try to redeploy 'as many staff internally as possible'
Prezzo to shut 46 restaurants putting 810 staff at risk - full list of sites closingThe move will put around 810 workers at risk of redundancy, the Italian restaurant chain said, although it will try to redeploy 'as many staff internally as possible'
Consulte Mais informação »
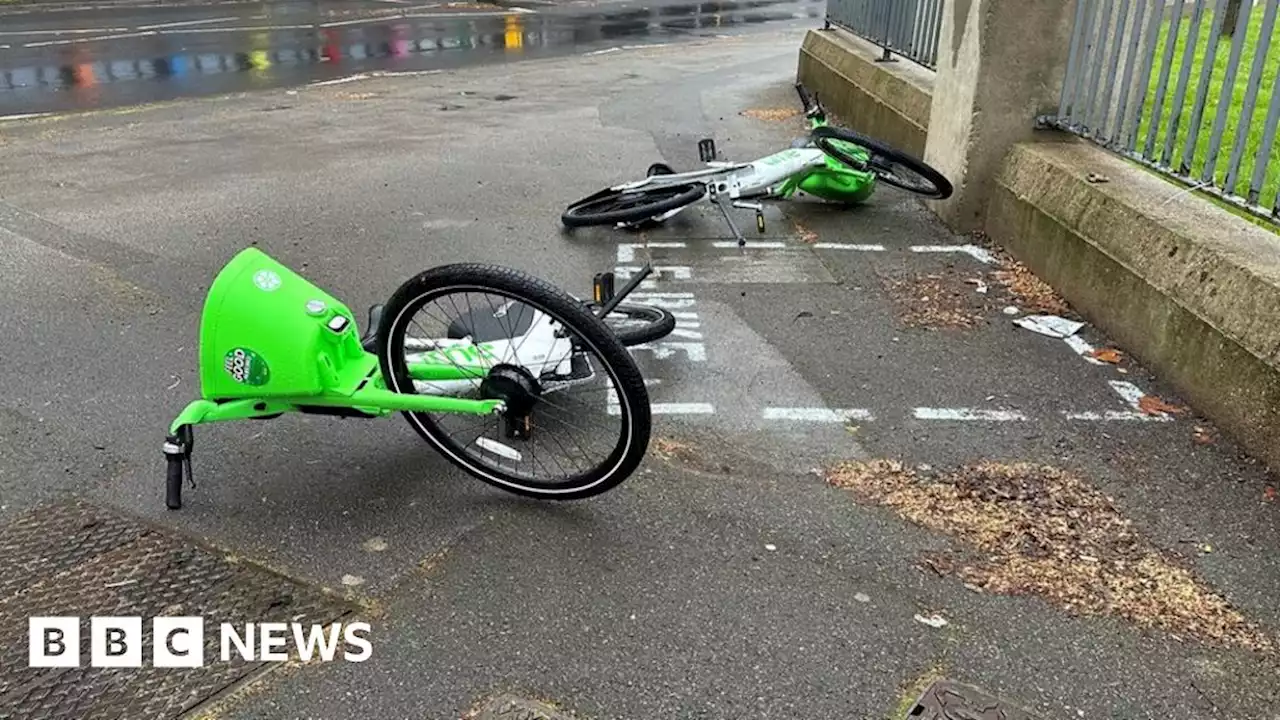 Nottingham: E-bikes putting blind people at risk, says charityA 700-bike scheme launched in Nottingham earlier this month is causing concern.
Nottingham: E-bikes putting blind people at risk, says charityA 700-bike scheme launched in Nottingham earlier this month is causing concern.
Consulte Mais informação »
