In a large retrospective analysis using measurements of thousands of plasma proteins in primary and secondary event populations, scientists from deCODE genetics and collaborators from U.S., Denmark and Iceland, reported today in JAMA how they employed AI to develop a protein score to predict major atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease events (ASCVD).
. A large part of the risk captured by the proteins is also captured by established risk factors, however, the protein score captures additional risk.
What is more, the protein risk score is a dynamic measure and as such has the potential of being modified upon treatment unlike some of the classic risk factors that are immutable, such as family history and prior ASCVD events. This dynamic feature of protein risk scores, that the levels of proteins rise and fall as a function of time to and from events, makes it well-suited to predict the timing of events.
"We believe that in the proteomic risk score, we may have a biomarker that will allow the world to conduct shorter clinical trials with fewer participants. This is going to make the development of new medicines less expensive and make them available sooner for those who need them. Furthermore, in it may allow for more effective prevention of ASCVD," said Kari Stefansson, CEO of deCODE genetics and one of the senior investigators of the study.Hannes Helgason et al, Evaluation of Large-Scale Proteomics for Prediction of Cardiovascular Events,
Brasil Últimas Notícias, Brasil Manchetes
Similar News:Você também pode ler notícias semelhantes a esta que coletamos de outras fontes de notícias.
 Heinz are selling new tomato ketchup-filled hash browns at IcelandHeinz is bringing together another iconic duo from the Great British breakfast
Heinz are selling new tomato ketchup-filled hash browns at IcelandHeinz is bringing together another iconic duo from the Great British breakfast
Consulte Mais informação »
 Iceland's new £3 snack that combines two 'breakfast legends'The new frozen snack is available in stores now
Iceland's new £3 snack that combines two 'breakfast legends'The new frozen snack is available in stores now
Consulte Mais informação »
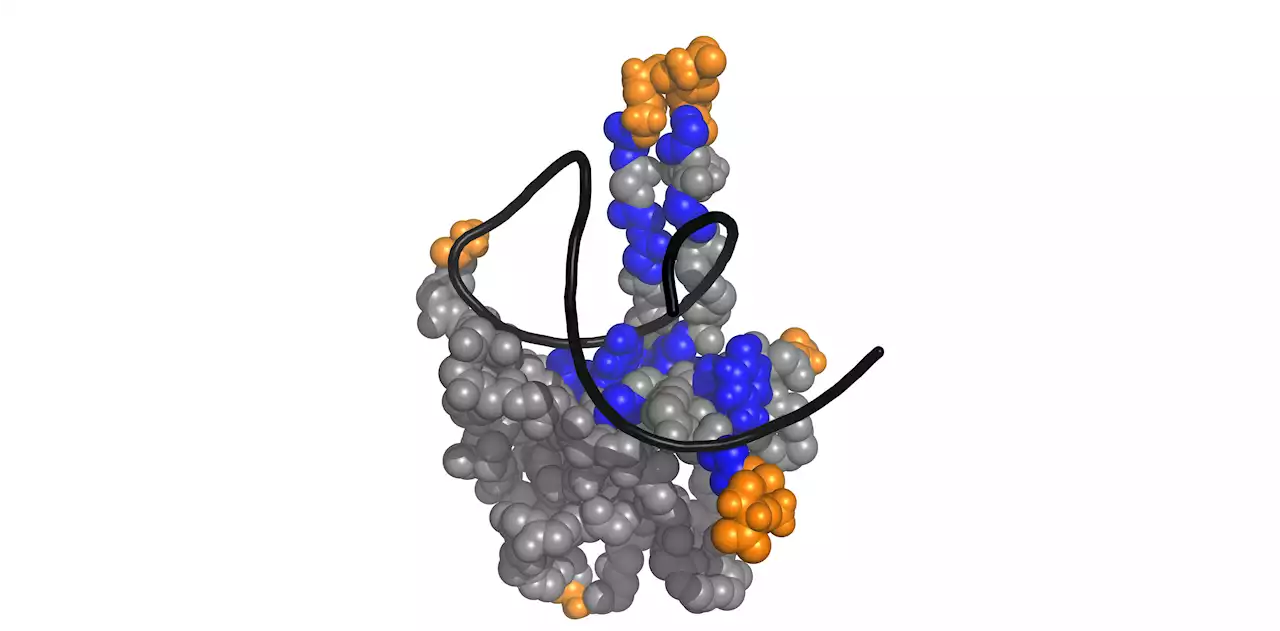 SARS-CoV-2: The grasping fingers of the viral N proteinImmediately after the infection of a cell in the throat or lungs, the SARS-CoV-2 virus works very hard to replicate, using the human cell's metabolic pathways to produce its proteins and make sure that its genetic material (the RNA genome) is copied. The RNA genome is then packaged very compactly into new virus particles that are released from the cell to infect more cells.
SARS-CoV-2: The grasping fingers of the viral N proteinImmediately after the infection of a cell in the throat or lungs, the SARS-CoV-2 virus works very hard to replicate, using the human cell's metabolic pathways to produce its proteins and make sure that its genetic material (the RNA genome) is copied. The RNA genome is then packaged very compactly into new virus particles that are released from the cell to infect more cells.
Consulte Mais informação »
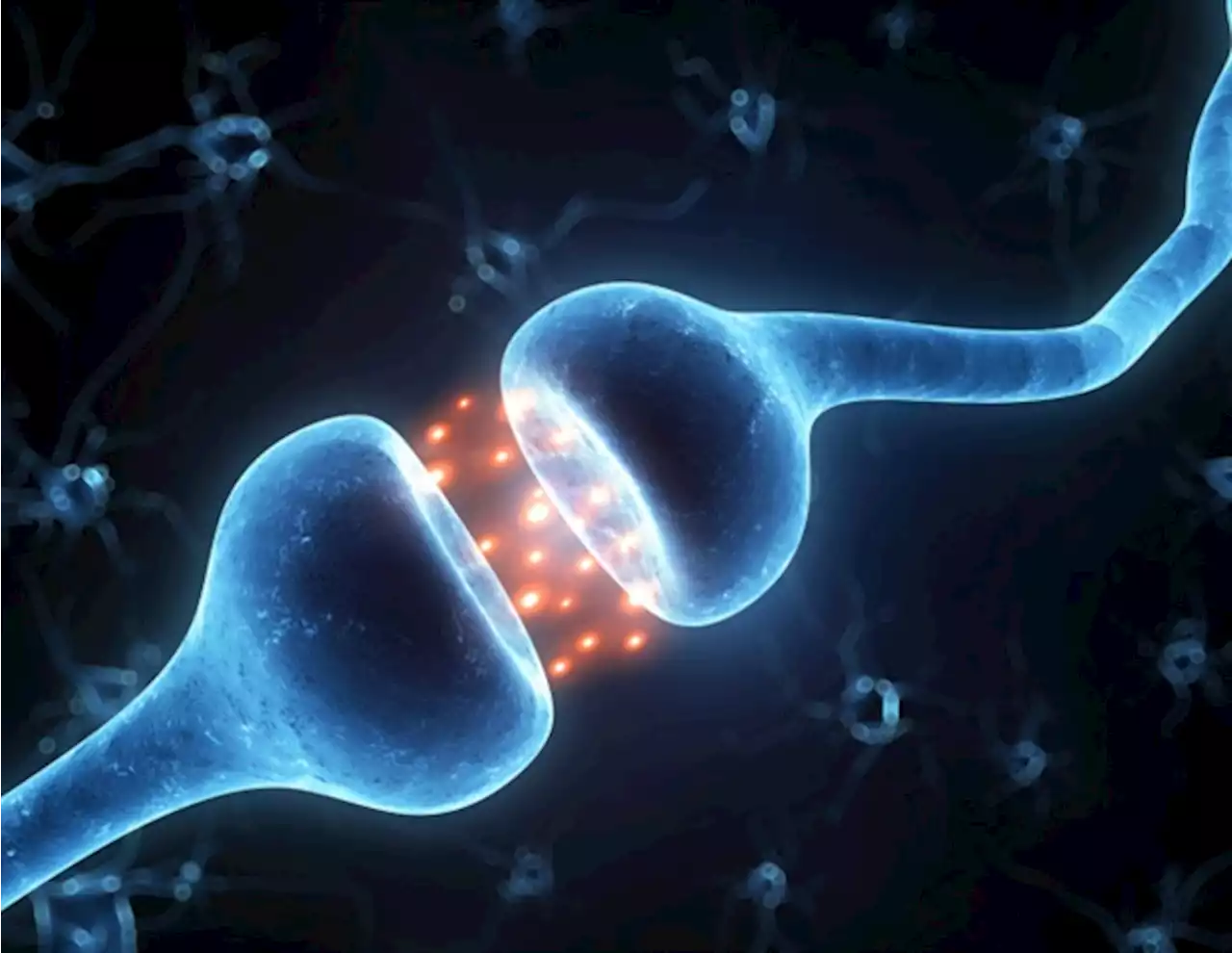 Melatonin enhances long-term memory by modulating protein phosphorylationMultiple studies have demonstrated the memory-enhancing effects of melatonin and its derivatives in animal models. It is also known that the formation of both short- and long-term memories require the phosphorylation of certain memory-related proteins.
Melatonin enhances long-term memory by modulating protein phosphorylationMultiple studies have demonstrated the memory-enhancing effects of melatonin and its derivatives in animal models. It is also known that the formation of both short- and long-term memories require the phosphorylation of certain memory-related proteins.
Consulte Mais informação »
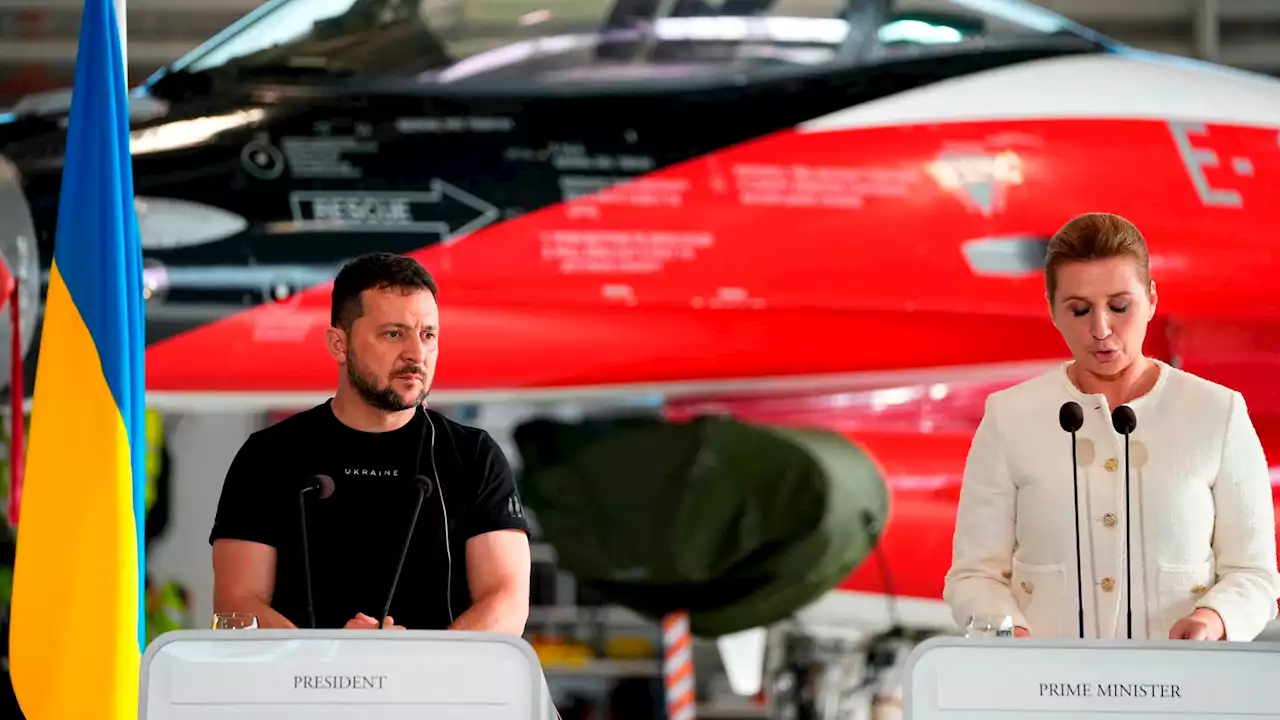 Netherlands and Denmark confirm plans to provide Kyiv with first F-16sLengthy pilot training process means fighter jets are unlikely to arrive in time to bolster summer counteroffensive
Netherlands and Denmark confirm plans to provide Kyiv with first F-16sLengthy pilot training process means fighter jets are unlikely to arrive in time to bolster summer counteroffensive
Consulte Mais informação »
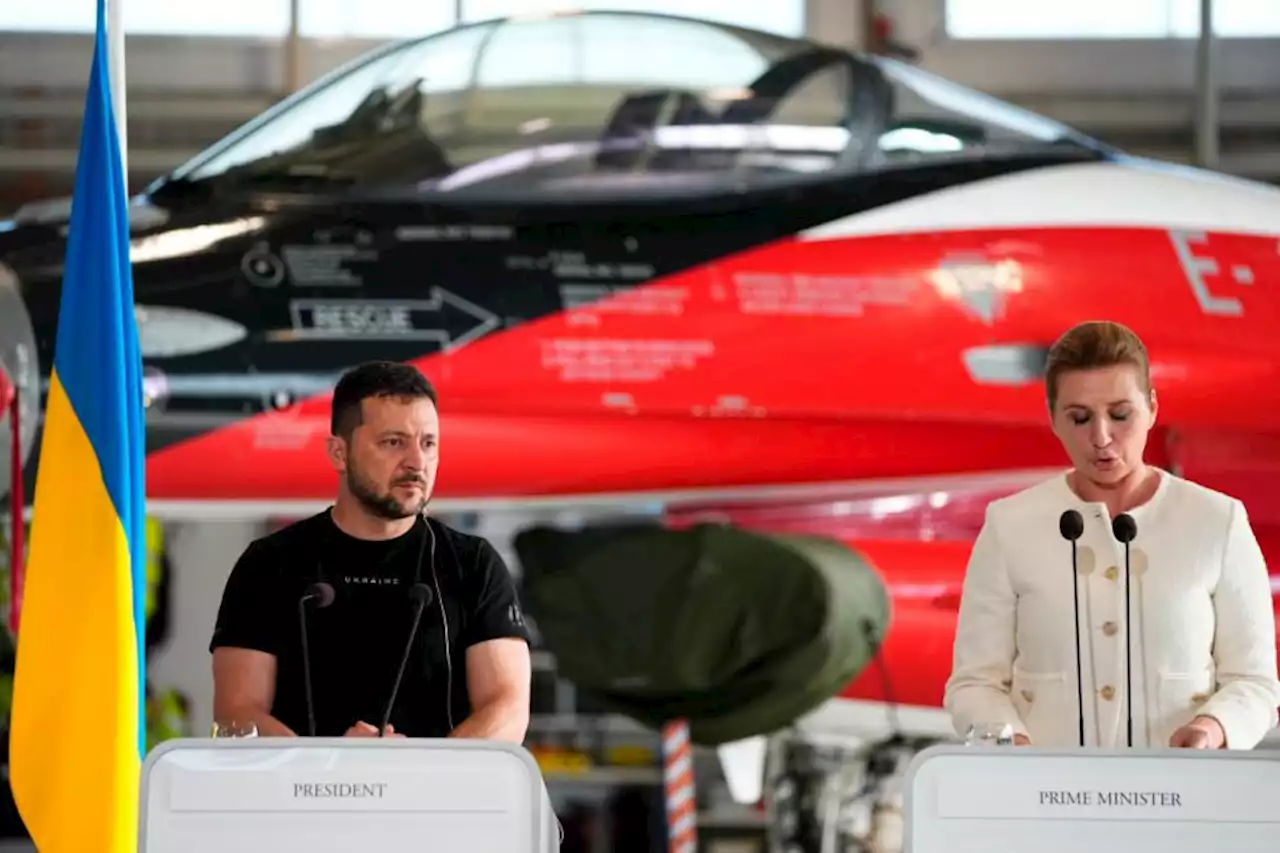 Denmark joins Netherlands in offering F-16 jets to Ukraine as Zelensky visitsUkrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky travelled to both countries Sunday to finalise the delivery deals.
Denmark joins Netherlands in offering F-16 jets to Ukraine as Zelensky visitsUkrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky travelled to both countries Sunday to finalise the delivery deals.
Consulte Mais informação »
