PATIENTS were unable to book GP appointments up to five million times last month, according to an analysis. The Labour Party said one in seven phone calls cannot get a consultation with a doctor. W…
PATIENTS were unable to book GP appointments up to five million times last month, according to an analysis.Patients were unable to book GP appointments up to five million times in October, according to an analysisWith almost 32million appointments in October, it suggests as many as 5.
2m calls did not get a slot.GP appointment“I’m really worried that among those patients unable to get an appointment, there could be serious conditions going undiagnosed until it’s too late.”Patient Survey this year found 13.8 per cent of people were not offered or refused a GP appointment last time they phoned for one.
Brasil Últimas Notícias, Brasil Manchetes
Similar News:Você também pode ler notícias semelhantes a esta que coletamos de outras fontes de notícias.
 Admission glucose as a prognostic marker for all-cause mortality and cardiovascular disease - Cardiovascular DiabetologyBackground Diabetes and prediabetes are known risk factors for cardiovascular disease and associated with increased mortality risk. Whether patients with a random elevated blood glucose level but no history of diabetes are at a higher mortality and cardiovascular risk is not entirely known. Methods A retrospective cohort study where patients (18–80 years) with no history of diabetes between 2006 and 2016 attending the emergency department (ED) in Sweden were included. Based on the first (index) blood glucose level patients were categorized into four groups: hypoglycemia ( 11.1 mmol/L). Data was collected from four nationwide registers (National Patient Register, National Cause of Death Register, Prescribed Drug Register and Statistics Sweden). Cox regression was used to calculate adjusted hazard ratios (HR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) for all-cause mortality and cardiovascular outcomes using NGT as reference. Results 618,694 patients were included during a mean follow-up time of 3.9 years. According to the index blood glucose level: 1871 (0.3%) had hypoglycemia, 525,636 (85%) had NGT, 77,442 (13%) had dysglycemia, and 13,745 (2%) patients had hyperglycemia, respectively. During follow-up 44,532 (7.2%) deaths occurred. After multiple adjustments, mortality risk was highest in patients with hypoglycemia HR 2.58 (2.26–2.96) followed by patients with hyperglycemia HR 1.69 (1.63–1.76) and dysglycemia HR 1.16 (1.13–1.19). Risk for cardiovascular events: i.e., myocardial infarction, stroke and heart failure, were highest among patients with hyperglycemia HR 2.28 (2.13–2.44), HR 1.62 (1.51–1.74) and HR 1.60 (1.46–1.75), respectively. Conclusion Patients with disturbed blood glucose level at ED admission have a higher mortality risk than patients with NGT. Patients with hyperglycemia have almost a two folded increased long-term mortality risk and more than a doubled risk for cardiovascular events compared to patients with NGT.
Admission glucose as a prognostic marker for all-cause mortality and cardiovascular disease - Cardiovascular DiabetologyBackground Diabetes and prediabetes are known risk factors for cardiovascular disease and associated with increased mortality risk. Whether patients with a random elevated blood glucose level but no history of diabetes are at a higher mortality and cardiovascular risk is not entirely known. Methods A retrospective cohort study where patients (18–80 years) with no history of diabetes between 2006 and 2016 attending the emergency department (ED) in Sweden were included. Based on the first (index) blood glucose level patients were categorized into four groups: hypoglycemia ( 11.1 mmol/L). Data was collected from four nationwide registers (National Patient Register, National Cause of Death Register, Prescribed Drug Register and Statistics Sweden). Cox regression was used to calculate adjusted hazard ratios (HR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) for all-cause mortality and cardiovascular outcomes using NGT as reference. Results 618,694 patients were included during a mean follow-up time of 3.9 years. According to the index blood glucose level: 1871 (0.3%) had hypoglycemia, 525,636 (85%) had NGT, 77,442 (13%) had dysglycemia, and 13,745 (2%) patients had hyperglycemia, respectively. During follow-up 44,532 (7.2%) deaths occurred. After multiple adjustments, mortality risk was highest in patients with hypoglycemia HR 2.58 (2.26–2.96) followed by patients with hyperglycemia HR 1.69 (1.63–1.76) and dysglycemia HR 1.16 (1.13–1.19). Risk for cardiovascular events: i.e., myocardial infarction, stroke and heart failure, were highest among patients with hyperglycemia HR 2.28 (2.13–2.44), HR 1.62 (1.51–1.74) and HR 1.60 (1.46–1.75), respectively. Conclusion Patients with disturbed blood glucose level at ED admission have a higher mortality risk than patients with NGT. Patients with hyperglycemia have almost a two folded increased long-term mortality risk and more than a doubled risk for cardiovascular events compared to patients with NGT.
Consulte Mais informação »
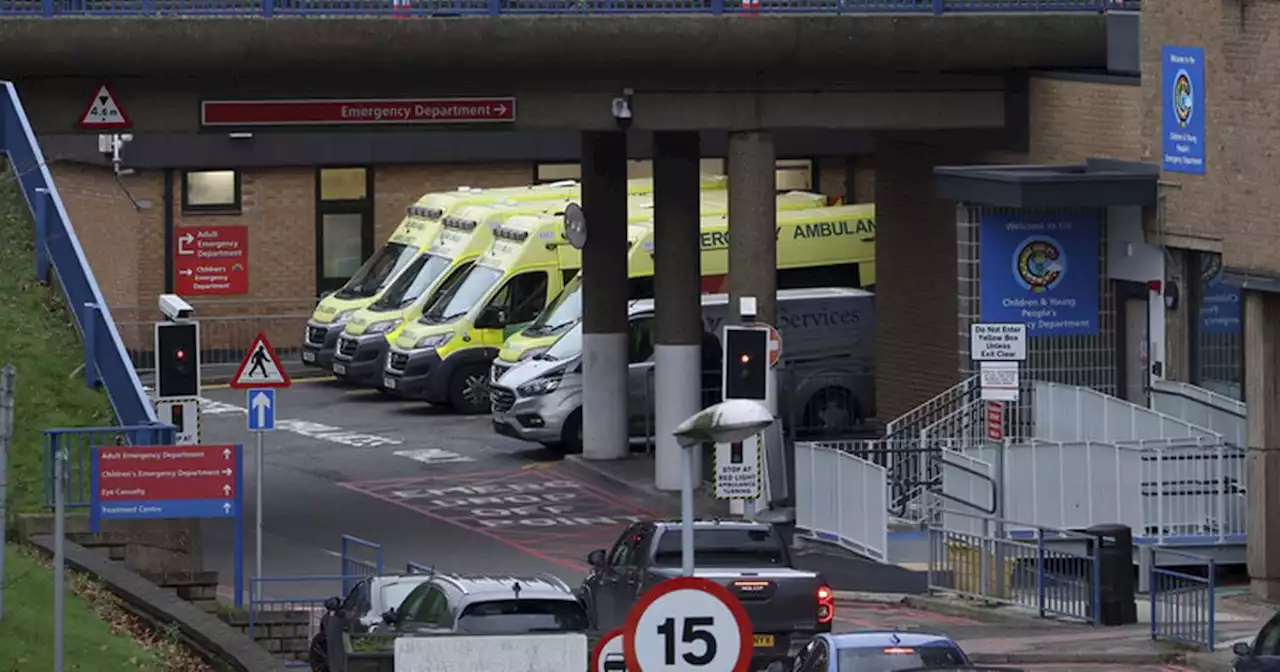 Trust apologises to patients asked to wait in A&E corridorsLetters, handed to a small number of Queen’s Medical Centre patients in recent days, explain how soaring demand is affecting A&E, wards and ambulance services
Trust apologises to patients asked to wait in A&E corridorsLetters, handed to a small number of Queen’s Medical Centre patients in recent days, explain how soaring demand is affecting A&E, wards and ambulance services
Consulte Mais informação »
 Study explores histopathological, serological, and clinical characteristics of PASC in patients with mild COVID-19Researchers investigated the clinical, histopathological, imaging, and serological characteristics of post-acute sequelae of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) (PASC) in patients with mild COVID-19.
Study explores histopathological, serological, and clinical characteristics of PASC in patients with mild COVID-19Researchers investigated the clinical, histopathological, imaging, and serological characteristics of post-acute sequelae of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) (PASC) in patients with mild COVID-19.
Consulte Mais informação »
 Co-infecting pathogens and the microbiome from SARS-CoV-2 positive and negative samplesCo-infecting pathogens and the microbiome from SARS-CoV-2 positive and negative samples PLOSONE jgi pathogen microbiome SARSCoV2 COVID19 coronavirus covid
Co-infecting pathogens and the microbiome from SARS-CoV-2 positive and negative samplesCo-infecting pathogens and the microbiome from SARS-CoV-2 positive and negative samples PLOSONE jgi pathogen microbiome SARSCoV2 COVID19 coronavirus covid
Consulte Mais informação »
 Epigenetic and transcriptomic reprogramming in monocytes of severe COVID-19 patients reflects alterations in myeloid differentiation and the influence of inflammatory cytokines - Genome MedicineBackground COVID-19 manifests with a wide spectrum of clinical phenotypes, ranging from asymptomatic and mild to severe and critical. Severe and critical COVID-19 patients are characterized by marked changes in the myeloid compartment, especially monocytes. However, little is known about the epigenetic alterations that occur in these cells during hyperinflammatory responses in severe COVID-19 patients. Methods In this study, we obtained the DNA methylome and transcriptome of peripheral blood monocytes from severe COVID-19 patients. DNA samples extracted from CD14 + CD15- monocytes of 48 severe COVID-19 patients and 11 healthy controls were hybridized on MethylationEPIC BeadChip arrays. In parallel, single-cell transcriptomics of 10 severe COVID-19 patients were generated. CellPhoneDB was used to infer changes in the crosstalk between monocytes and other immune cell types. Results We observed DNA methylation changes in CpG sites associated with interferon-related genes and genes associated with antigen presentation, concordant with gene expression changes. These changes significantly overlapped with those occurring in bacterial sepsis, although specific DNA methylation alterations in genes specific to viral infection were also identified. We also found these alterations to comprise some of the DNA methylation changes occurring during myeloid differentiation and under the influence of inflammatory cytokines. A progression of DNA methylation alterations in relation to the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score was found to be related to interferon-related genes and T-helper 1 cell cytokine production. CellPhoneDB analysis of the single-cell transcriptomes of other immune cell types suggested the existence of altered crosstalk between monocytes and other cell types like NK cells and regulatory T cells. Conclusion Our findings show the occurrence of an epigenetic and transcriptional reprogramming of peripheral blood monocytes, which could be associated with the
Epigenetic and transcriptomic reprogramming in monocytes of severe COVID-19 patients reflects alterations in myeloid differentiation and the influence of inflammatory cytokines - Genome MedicineBackground COVID-19 manifests with a wide spectrum of clinical phenotypes, ranging from asymptomatic and mild to severe and critical. Severe and critical COVID-19 patients are characterized by marked changes in the myeloid compartment, especially monocytes. However, little is known about the epigenetic alterations that occur in these cells during hyperinflammatory responses in severe COVID-19 patients. Methods In this study, we obtained the DNA methylome and transcriptome of peripheral blood monocytes from severe COVID-19 patients. DNA samples extracted from CD14 + CD15- monocytes of 48 severe COVID-19 patients and 11 healthy controls were hybridized on MethylationEPIC BeadChip arrays. In parallel, single-cell transcriptomics of 10 severe COVID-19 patients were generated. CellPhoneDB was used to infer changes in the crosstalk between monocytes and other immune cell types. Results We observed DNA methylation changes in CpG sites associated with interferon-related genes and genes associated with antigen presentation, concordant with gene expression changes. These changes significantly overlapped with those occurring in bacterial sepsis, although specific DNA methylation alterations in genes specific to viral infection were also identified. We also found these alterations to comprise some of the DNA methylation changes occurring during myeloid differentiation and under the influence of inflammatory cytokines. A progression of DNA methylation alterations in relation to the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score was found to be related to interferon-related genes and T-helper 1 cell cytokine production. CellPhoneDB analysis of the single-cell transcriptomes of other immune cell types suggested the existence of altered crosstalk between monocytes and other cell types like NK cells and regulatory T cells. Conclusion Our findings show the occurrence of an epigenetic and transcriptional reprogramming of peripheral blood monocytes, which could be associated with the
Consulte Mais informação »
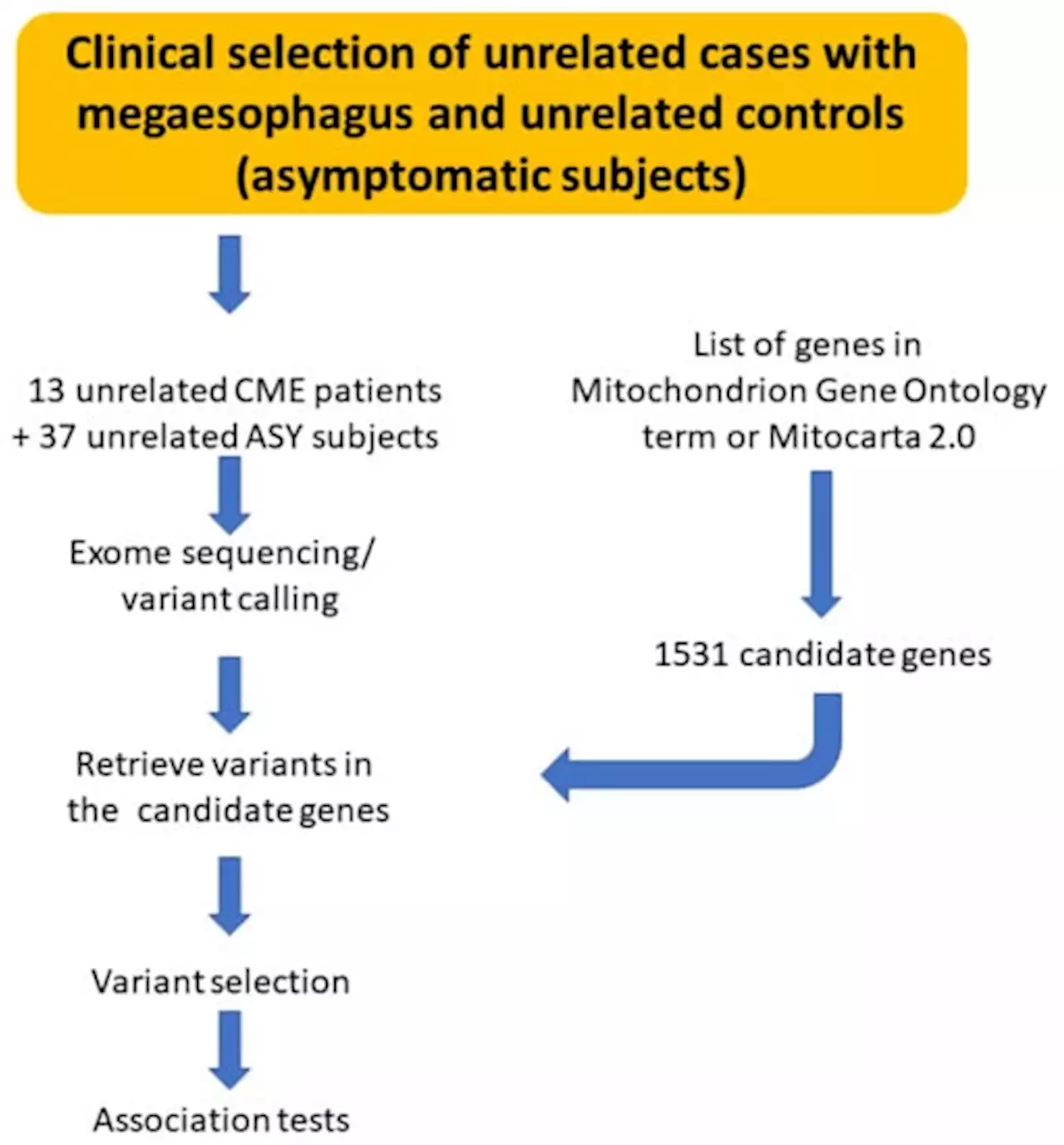 Chagas Disease Megaesophagus Patients Carrying Variant MRPS18B P260A Display Nitro-Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Response to IFN-γ StimulusChagas disease (CD), caused by the protozoan parasite Trypanosoma cruzi, affects 8 million people, and around 1/3 develop chronic cardiac (CCC) or digestive disease (megaesophagus/megacolon), while the majority remain asymptomatic, in the indeterminate form of Chagas disease (ASY). Most CCC cases in families with multiple Chagas disease patients carry damaging mutations in mitochondrial genes. We searched for exonic mutations associated to chagasic megaesophagus (CME) in genes essential to mitochondrial processes. We performed whole exome sequencing of 13 CME and 45 ASY patients. We found the damaging variant MRPS18B 688C > G P230A, in five out of the 13 CME patients (one of them being homozygous; 38.4%), while the variant appeared in one out of 45 ASY patients (2.2%). We analyzed the interferon (IFN)-γ-induced nitro-oxidative stress and mitochondrial function of EBV-transformed lymphoblastoid cell lines. We found the CME carriers of the mutation displayed increased levels of nitrite and nitrated proteins; in addition, the homozygous (G/G) CME patient also showed increased mitochondrial superoxide and reduced levels of ATP production. The results suggest that pathogenic mitochondrial mutations may contribute to cytokine-induced nitro-oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. We hypothesize that, in mutation carriers, IFN-γ produced in the esophageal myenteric plexus might cause nitro-oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in neurons, contributing to megaesophagus.
Chagas Disease Megaesophagus Patients Carrying Variant MRPS18B P260A Display Nitro-Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Response to IFN-γ StimulusChagas disease (CD), caused by the protozoan parasite Trypanosoma cruzi, affects 8 million people, and around 1/3 develop chronic cardiac (CCC) or digestive disease (megaesophagus/megacolon), while the majority remain asymptomatic, in the indeterminate form of Chagas disease (ASY). Most CCC cases in families with multiple Chagas disease patients carry damaging mutations in mitochondrial genes. We searched for exonic mutations associated to chagasic megaesophagus (CME) in genes essential to mitochondrial processes. We performed whole exome sequencing of 13 CME and 45 ASY patients. We found the damaging variant MRPS18B 688C > G P230A, in five out of the 13 CME patients (one of them being homozygous; 38.4%), while the variant appeared in one out of 45 ASY patients (2.2%). We analyzed the interferon (IFN)-γ-induced nitro-oxidative stress and mitochondrial function of EBV-transformed lymphoblastoid cell lines. We found the CME carriers of the mutation displayed increased levels of nitrite and nitrated proteins; in addition, the homozygous (G/G) CME patient also showed increased mitochondrial superoxide and reduced levels of ATP production. The results suggest that pathogenic mitochondrial mutations may contribute to cytokine-induced nitro-oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. We hypothesize that, in mutation carriers, IFN-γ produced in the esophageal myenteric plexus might cause nitro-oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in neurons, contributing to megaesophagus.
Consulte Mais informação »
