New insights into the driving factors of COVID-19 dynamics in England England Coronavirus Disease COVID Epidemiology medrxivpreprint imperialcollege RBandH Cambridge_Uni LSHTM NIHRresearch
SARS-CoV-2 infections have led to unprecedented morbidity and mortality across the globe, and the continual emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants has made COVID-19 mitigation challenging. Epidemiological analyses have been performed to assess SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern transmissibility and the severity of infections caused by them. However, integrated analyses quantifying the effectiveness of various interventions and directly comparing VOC severity and transmissibility are limited.
Data analyzed included polymerase chain reaction reports, population-level COVID-19 prevalence survey data, genomic characterization of PCR-positive COVID-19 cases, seroprevalence data from blood donors’ residual serum samples, hospitalizations, and deaths at the individual level and community level. The relative and absolute transmissibility of SARS-CoV-2 wild-type strains and VOC, such as the Alpha VOC, Delta VOC, and Omicron VOC’s BA.1 sub-VOC were estimated.
Results Before COVID-19 vaccinations, Rtff was marginally lesser than Rt, indicating low prior infection-induced immune protection, and only stringent levels of NPIs were effective in curtailing SARS-CoV-2 transmission.
Transmissibility increased with every successive VOC, and BA.1 had the highest basic reproduction number at 8.1. In contrast to previous studies, Alpha VOC had the greatest basic IFR , followed by Delta , wild-type , and Omicron . The basic IHRs for the wild-type strain, Alpha VOC, Delta VOC, and Omicron VOC, were 2.20%, 3.50%, 4.40%, and 3.50%, respectively. The HFRs for the corresponding strains were 33%, 48%, 30%, and 11%, respectively.
Brasil Últimas Notícias, Brasil Manchetes
Similar News:Você também pode ler notícias semelhantes a esta que coletamos de outras fontes de notícias.
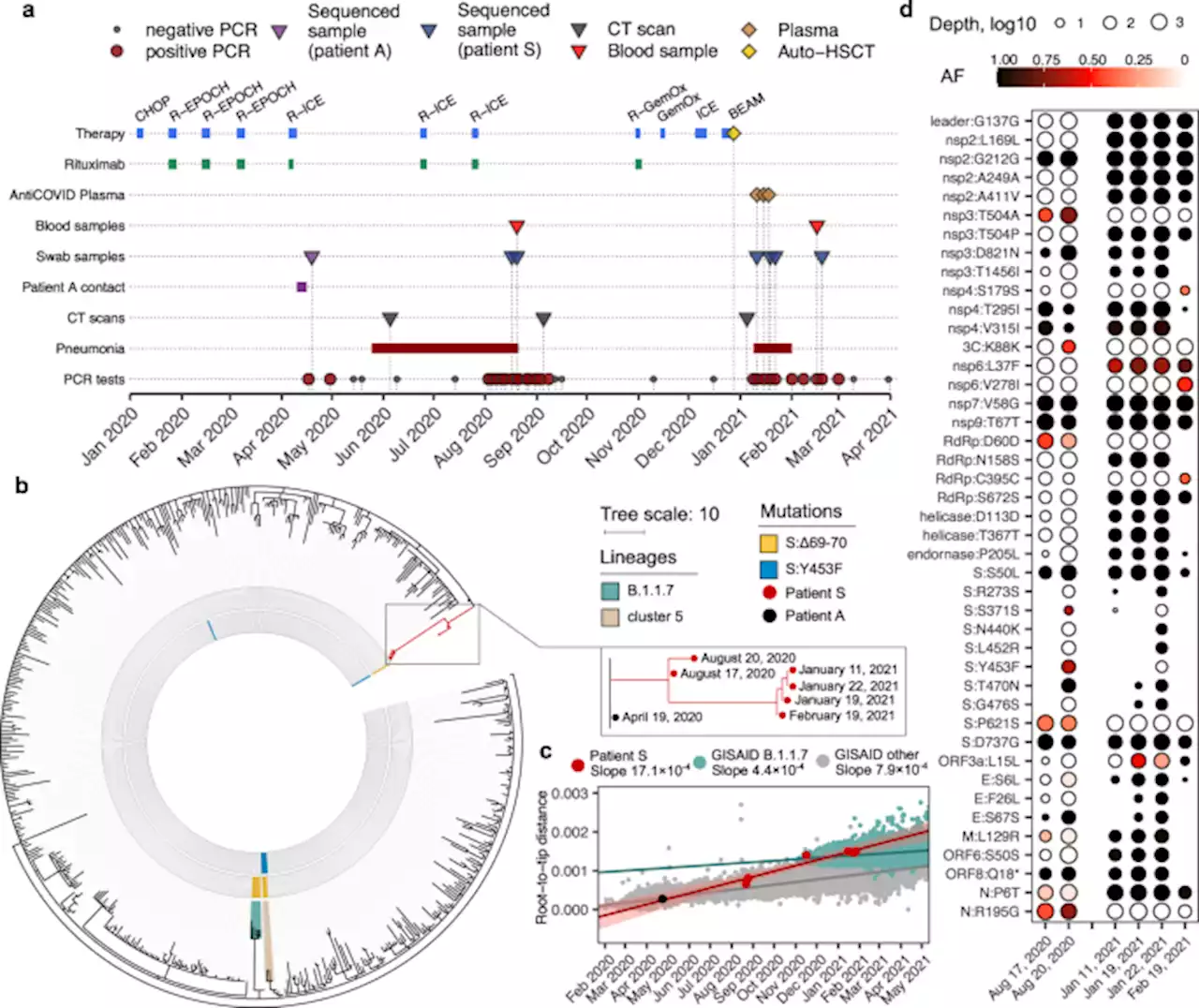 SARS-CoV-2 escape from cytotoxic T cells during long-term COVID-19 - Nature CommunicationsHere, the authors report accelerated intrahost evolution of SARS-CoV-2 in an immunocompromised patient with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma with 318 days long COVID-19, and show that changes in the viral genome resulted in escape from T cellular immune response.
SARS-CoV-2 escape from cytotoxic T cells during long-term COVID-19 - Nature CommunicationsHere, the authors report accelerated intrahost evolution of SARS-CoV-2 in an immunocompromised patient with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma with 318 days long COVID-19, and show that changes in the viral genome resulted in escape from T cellular immune response.
Consulte Mais informação »
 Inflammation-associated gut microbiome in postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 points towards new therapeutic targetsWe read with interest the recent report by Liu et al 1 describing faecal microbiome differences with postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 (PASC), commonly referred to as ‘Long-COVID’. We have previously reported elevated levels of SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells with PASC compared with resolved COVID-19 (RC; no lingering symptoms at the time of sample collection) that correlated with increased levels of the inflammatory marker IL-6, suggesting that elevated inflammation in PASC may be related to immune response to residual virus.2 Although several studies have reported gut microbiome differences during acute COVID-19,3 PASC has received less attention. We, thus, sought to characterise gut microbiome differences in PASC versus RC using faecal samples from our study2 and to relate these differences to inflammation. The faecal microbiome was evaluated using 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Plasma levels of inflammatory markers IL-6 and C reactive protein (CRP) were measured with ELISA (see online supplemental methods). Cohort information is in table 1. IL-6 and CRP were elevated with PASC (figure 1A). Gut microbiome composition did not significantly differ between the PASC and RC cohorts (PERMANOVA; p=0.087; figure 1B), but did correlate with IL-6 and CRP levels (Adonis; IL-6 p=0.03; CRP p=0.01). IL-6 and CRP also correlated with PC1 from a principal coordinates analysis (figure 1C,D), suggesting a relationship between microbiome composition and inflammation in PASC. Using SELBAL,4 which identifies ratios …
Inflammation-associated gut microbiome in postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 points towards new therapeutic targetsWe read with interest the recent report by Liu et al 1 describing faecal microbiome differences with postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 (PASC), commonly referred to as ‘Long-COVID’. We have previously reported elevated levels of SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells with PASC compared with resolved COVID-19 (RC; no lingering symptoms at the time of sample collection) that correlated with increased levels of the inflammatory marker IL-6, suggesting that elevated inflammation in PASC may be related to immune response to residual virus.2 Although several studies have reported gut microbiome differences during acute COVID-19,3 PASC has received less attention. We, thus, sought to characterise gut microbiome differences in PASC versus RC using faecal samples from our study2 and to relate these differences to inflammation. The faecal microbiome was evaluated using 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Plasma levels of inflammatory markers IL-6 and C reactive protein (CRP) were measured with ELISA (see online supplemental methods). Cohort information is in table 1. IL-6 and CRP were elevated with PASC (figure 1A). Gut microbiome composition did not significantly differ between the PASC and RC cohorts (PERMANOVA; p=0.087; figure 1B), but did correlate with IL-6 and CRP levels (Adonis; IL-6 p=0.03; CRP p=0.01). IL-6 and CRP also correlated with PC1 from a principal coordinates analysis (figure 1C,D), suggesting a relationship between microbiome composition and inflammation in PASC. Using SELBAL,4 which identifies ratios …
Consulte Mais informação »
 Stokes announces return of Broad for England's first Test against New ZealandBen Stokes has announced that Stuart Broad will return to England’s line-up for the first Test against New Zealand as the touring side look to take their BazBall adventure even further. Stokes’ lin…
Stokes announces return of Broad for England's first Test against New ZealandBen Stokes has announced that Stuart Broad will return to England’s line-up for the first Test against New Zealand as the touring side look to take their BazBall adventure even further. Stokes’ lin…
Consulte Mais informação »
 New roads scrapped in Wales to hit net-zero, putting pressure on England to followTwo dozen new roads are being cancelled or delayed in Wales to discourage driving and reduce carbon emissions, the Welsh Government has announced
New roads scrapped in Wales to hit net-zero, putting pressure on England to followTwo dozen new roads are being cancelled or delayed in Wales to discourage driving and reduce carbon emissions, the Welsh Government has announced
Consulte Mais informação »
 Waters Off New England Had 2nd Warmest Year on Record in 2022The waters off New England logged the second-warmest year in their recorded history last year. The Gulf of Maine, a body of water about the size of Indiana that touches Maine, New Hampshire, Massachusetts and Canada, is warming faster than the vast majority of the world’s oceans. Scientists with Gulf of Maine Research Institute, a science center in Portland say last year fell short of setting a new high mark for hottest year in record by less than half a degree Fahrenheit. The average sea surface temperature was 53.66 degrees Fahrenheit, more than 3.7 degrees above the 40-year average.
Waters Off New England Had 2nd Warmest Year on Record in 2022The waters off New England logged the second-warmest year in their recorded history last year. The Gulf of Maine, a body of water about the size of Indiana that touches Maine, New Hampshire, Massachusetts and Canada, is warming faster than the vast majority of the world’s oceans. Scientists with Gulf of Maine Research Institute, a science center in Portland say last year fell short of setting a new high mark for hottest year in record by less than half a degree Fahrenheit. The average sea surface temperature was 53.66 degrees Fahrenheit, more than 3.7 degrees above the 40-year average.
Consulte Mais informação »
 The impact of COVID-19 on consultations and antibiotic prescribing for URTI in EnglandIn a recent study published in the journal JAC-Antimicrobial Resistance, researchers investigated the trends in antibiotic prescriptions for upper respiratory tract infections to determine whether the decrease in in-person medical consultation appointments during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic had an impact on the prescribing practices.
The impact of COVID-19 on consultations and antibiotic prescribing for URTI in EnglandIn a recent study published in the journal JAC-Antimicrobial Resistance, researchers investigated the trends in antibiotic prescriptions for upper respiratory tract infections to determine whether the decrease in in-person medical consultation appointments during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic had an impact on the prescribing practices.
Consulte Mais informação »
