Researchers may have found a new biomarker for acute COVID-19 frontiersin
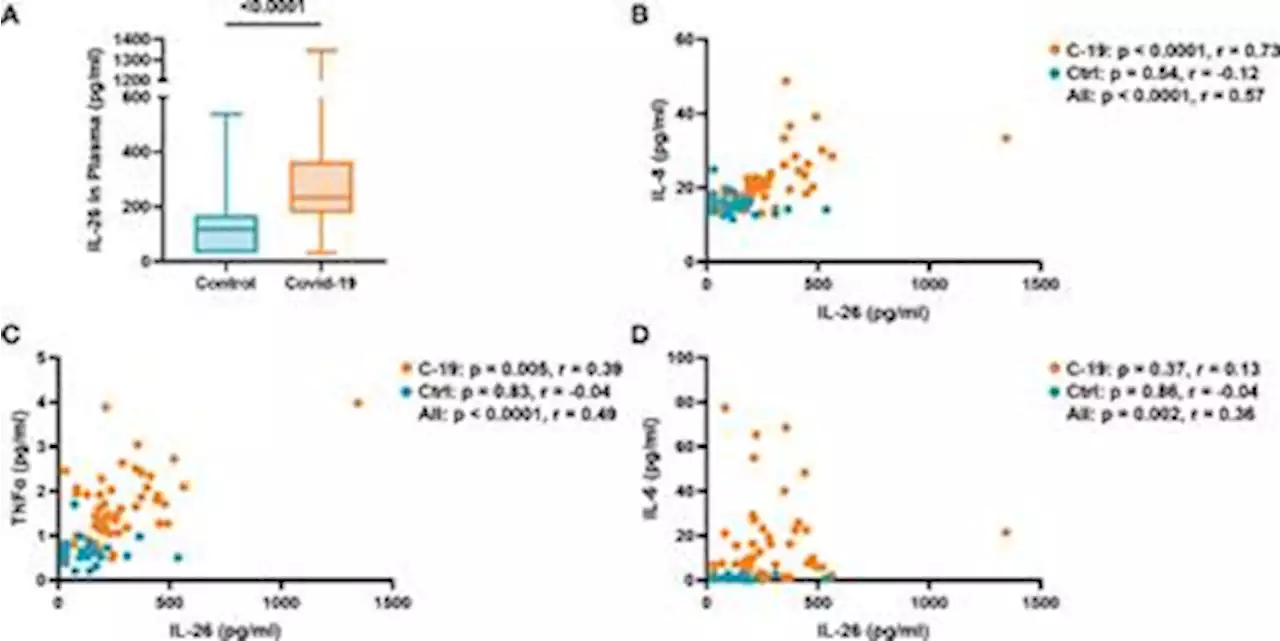
). Taken together, these findings are suggestive of a mechanistic link between IL-26 and severe COVID-19 that deserves further investigation in larger study materials.
It is true that a previous study by Caterino M. et al. failed to detect differences in the serum concentrations of IL-26 among COVID-19 patients with mild, moderate, or severe disease. However, their study did not include healthy control subjects. We think that their uncontrolled approach contributed to the failure to obtain evidence for the involvement of IL-26 in COVID-19. Furthermore, the fact that Caterino M. et al.
In summary, our current pilot study forwards evidence that systemic IL-26 is markedly increased in patients with acute COVID-19, and that it correlates with neutrophil-mobilizing cytokines, a marker of prolonged neutrophil survival, and with markers of tissue damage and hematological alteration, the latter of which are known to signify severe COVID-19.
Brasil Últimas Notícias, Brasil Manchetes
Similar News:Você também pode ler notícias semelhantes a esta que coletamos de outras fontes de notícias.
 SSPH+ | The Real-World Impact of Vaccination on COVID-19 Cases During Europe’s Fourth WaveBackground Disease control is important to limit the social, economic and health effects of COVID-19 and reduce the risk of novel variants emerging. Evidence suggests vaccines are less effective against the Omicron variant, but their impact on disease control is unclear. Methods We used a longitudinal fixed effects Poisson regression model to assess the impact of vaccination on COVID-19 case rates across 32 countries in Europe from 13th October to 01st January 2022. We controlled for country and time fixed effects and the severity of public health restrictions. Results Full vaccination coverage increased by 4.2%, leading to a 54% reduction in case rates across Europe (p|0.001). This protection decreased over time but remained significant at five weeks after the detection of Omicron. Mean booster vaccination rates increased from 2.71% to 24.5% but provided no significant additional benefit. For every one-unit increase in the severity of public health restrictions, case rates fell by a further 2% (p=0.019). Conclusions Full vaccination significantly limited the spread of COVID-19 and blunted the impact of the Omicron variant, despite becoming less useful over time.
SSPH+ | The Real-World Impact of Vaccination on COVID-19 Cases During Europe’s Fourth WaveBackground Disease control is important to limit the social, economic and health effects of COVID-19 and reduce the risk of novel variants emerging. Evidence suggests vaccines are less effective against the Omicron variant, but their impact on disease control is unclear. Methods We used a longitudinal fixed effects Poisson regression model to assess the impact of vaccination on COVID-19 case rates across 32 countries in Europe from 13th October to 01st January 2022. We controlled for country and time fixed effects and the severity of public health restrictions. Results Full vaccination coverage increased by 4.2%, leading to a 54% reduction in case rates across Europe (p|0.001). This protection decreased over time but remained significant at five weeks after the detection of Omicron. Mean booster vaccination rates increased from 2.71% to 24.5% but provided no significant additional benefit. For every one-unit increase in the severity of public health restrictions, case rates fell by a further 2% (p=0.019). Conclusions Full vaccination significantly limited the spread of COVID-19 and blunted the impact of the Omicron variant, despite becoming less useful over time.
Consulte Mais informação »
 Covid Bereavement Group Fly Banner With Message For Matt Hancock Over I'm A Celebrity Jungle'He isn’t a ‘celebrity’... he oversaw the UK having one of the highest death tolls in the world from Covid-19 whilst breaking his own lockdown rules,' the group said.
Covid Bereavement Group Fly Banner With Message For Matt Hancock Over I'm A Celebrity Jungle'He isn’t a ‘celebrity’... he oversaw the UK having one of the highest death tolls in the world from Covid-19 whilst breaking his own lockdown rules,' the group said.
Consulte Mais informação »
 Do SSRIs lower the risk of long COVID?Researchers conducted a retrospective study to determine whether SSRIs with immunomodulatory and antiplatelet properties can decrease the risk of post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC).
Do SSRIs lower the risk of long COVID?Researchers conducted a retrospective study to determine whether SSRIs with immunomodulatory and antiplatelet properties can decrease the risk of post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC).
Consulte Mais informação »
 Nicola Sturgeon urges Scots to get Covid vaccine as she receives her boosterNICOLA Sturgeon has urged all eligible Scots to get their Covid-19 vaccine as she received her booster.
Nicola Sturgeon urges Scots to get Covid vaccine as she receives her boosterNICOLA Sturgeon has urged all eligible Scots to get their Covid-19 vaccine as she received her booster.
Consulte Mais informação »
 Prevalence and severity of liver enzyme alterations in COVID-19 and association with patient-centered outcomesPrevalence and severity of liver enzyme alterations in COVID-19 and association with patient-centered outcomes medrxivpreprint georgeinstitute UniofOxford Univ_Lorraine COVID19 coronavirus covid liver enzyme
Prevalence and severity of liver enzyme alterations in COVID-19 and association with patient-centered outcomesPrevalence and severity of liver enzyme alterations in COVID-19 and association with patient-centered outcomes medrxivpreprint georgeinstitute UniofOxford Univ_Lorraine COVID19 coronavirus covid liver enzyme
Consulte Mais informação »