A systematic review published in BMCPsychiatry finds that mindfulness-based interventions improve brain function in chronic substance users in regions ascribed to substance-related stress, drug quantity, and cravings.
]. Presence/symptoms of mental health disorders were not systematically accounted for in the analyses, and therefore may have confounded the results.
Future studies should confirm how MBI-associated brain changes drive changes reported in the literature to date, in substance use/misuse, mental health and wellbeing, via careful measurement of these variables at all assessment points, and correlation of outcomes within intervention groups separately.
Brasil Últimas Notícias, Brasil Manchetes
Similar News:Você também pode ler notícias semelhantes a esta que coletamos de outras fontes de notícias.
 Disease-specific health spending by age, sex, and type of care in Norway: a national health registry study - BMC MedicineBackground Norway is a high-income nation with universal tax-financed health care and among the highest per person health spending in the world. This study estimates Norwegian health expenditures by health condition, age, and sex, and compares it with disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs). Methods Government budgets, reimbursement databases, patient registries, and prescription databases were combined to estimate spending for 144 health conditions, 38 age and sex groups, and eight types of care (GPs; physiotherapists & chiropractors; specialized outpatient; day patient; inpatient; prescription drugs; home-based care; and nursing homes) totaling 174,157,766 encounters. Diagnoses were in accordance with the Global Burden of Disease study (GBD). The spending estimates were adjusted, by redistributing excess spending associated with each comorbidity. Disease-specific DALYs were gathered from GBD 2019. Results The top five aggregate causes of Norwegian health spending in 2019 were mental and substance use disorders (20.7%), neurological disorders (15.4%), cardiovascular diseases (10.1%), diabetes, kidney, and urinary diseases (9.0%), and neoplasms (7.2%). Spending increased sharply with age. Among 144 health conditions, dementias had the highest health spending, with 10.2% of total spending, and 78% of this spending was incurred at nursing homes. The second largest was falls estimated at 4.6% of total spending. Spending in those aged 15–49 was dominated by mental and substance use disorders, with 46.0% of total spending. Accounting for longevity, spending per female was greater than spending per male, particularly for musculoskeletal disorders, dementias, and falls. Spending correlated well with DALYs (Correlation r = 0.77, 95% CI 0.67–0.87), and the correlation of spending with non-fatal disease burden (r = 0.83, 0.76–0.90) was more pronounced than with mortality (r = 0.58, 0.43–0.72). Conclusions Health spending was high for long-term disabilities in older age groups.
Disease-specific health spending by age, sex, and type of care in Norway: a national health registry study - BMC MedicineBackground Norway is a high-income nation with universal tax-financed health care and among the highest per person health spending in the world. This study estimates Norwegian health expenditures by health condition, age, and sex, and compares it with disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs). Methods Government budgets, reimbursement databases, patient registries, and prescription databases were combined to estimate spending for 144 health conditions, 38 age and sex groups, and eight types of care (GPs; physiotherapists & chiropractors; specialized outpatient; day patient; inpatient; prescription drugs; home-based care; and nursing homes) totaling 174,157,766 encounters. Diagnoses were in accordance with the Global Burden of Disease study (GBD). The spending estimates were adjusted, by redistributing excess spending associated with each comorbidity. Disease-specific DALYs were gathered from GBD 2019. Results The top five aggregate causes of Norwegian health spending in 2019 were mental and substance use disorders (20.7%), neurological disorders (15.4%), cardiovascular diseases (10.1%), diabetes, kidney, and urinary diseases (9.0%), and neoplasms (7.2%). Spending increased sharply with age. Among 144 health conditions, dementias had the highest health spending, with 10.2% of total spending, and 78% of this spending was incurred at nursing homes. The second largest was falls estimated at 4.6% of total spending. Spending in those aged 15–49 was dominated by mental and substance use disorders, with 46.0% of total spending. Accounting for longevity, spending per female was greater than spending per male, particularly for musculoskeletal disorders, dementias, and falls. Spending correlated well with DALYs (Correlation r = 0.77, 95% CI 0.67–0.87), and the correlation of spending with non-fatal disease burden (r = 0.83, 0.76–0.90) was more pronounced than with mortality (r = 0.58, 0.43–0.72). Conclusions Health spending was high for long-term disabilities in older age groups.
Consulte Mais informação »
 Unveiling ancient minds: fossil endocasts unlock secrets of past brainsUnveiling ancient minds: fossil endocasts unlock secrets of past brains NatureComms BathSpaUni fossils brainfossil unlock ancientminds
Unveiling ancient minds: fossil endocasts unlock secrets of past brainsUnveiling ancient minds: fossil endocasts unlock secrets of past brains NatureComms BathSpaUni fossils brainfossil unlock ancientminds
Consulte Mais informação »
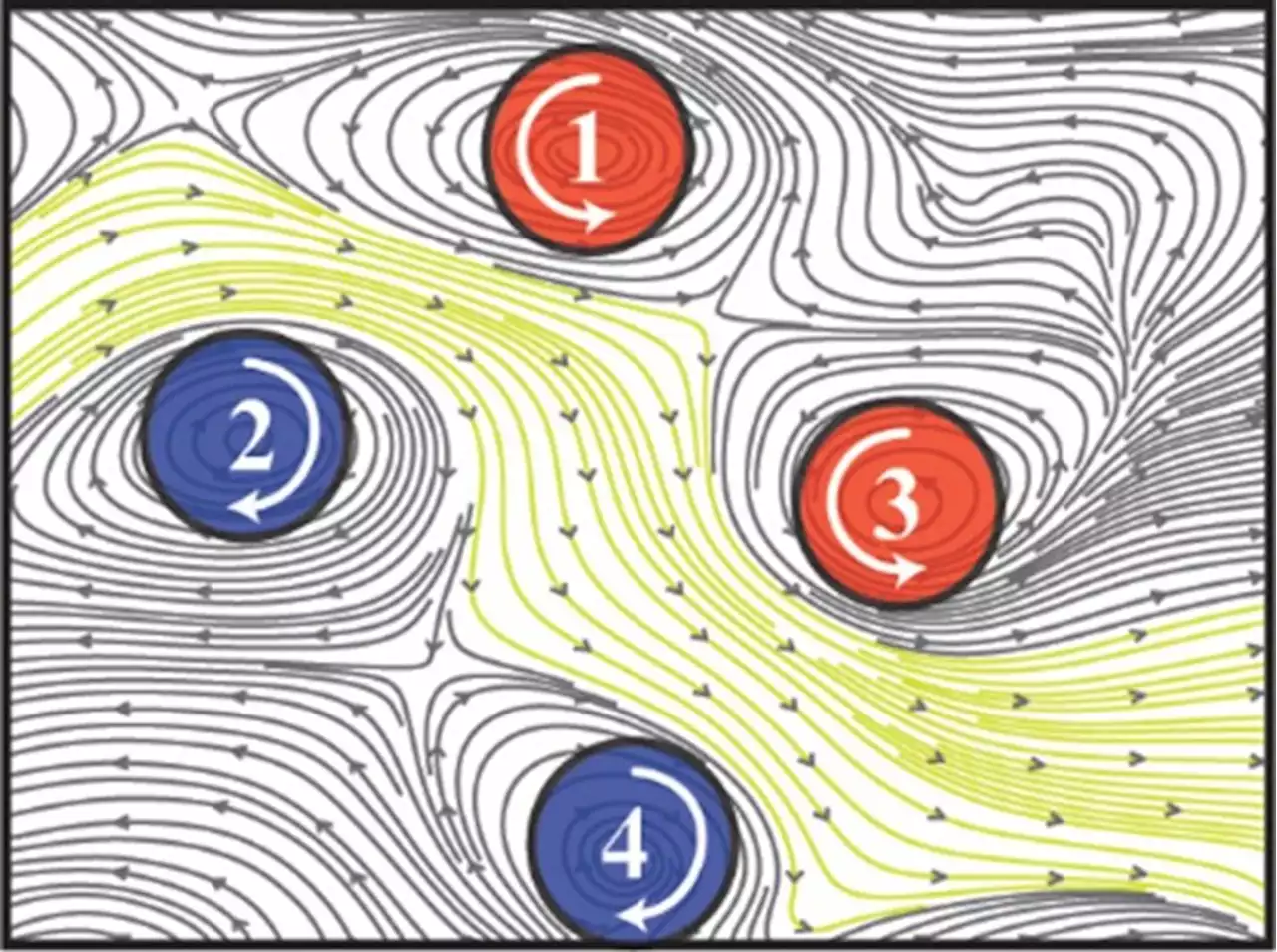 Scientists discover spiral-shaped signals that organize brain activityUniversity of Sydney and Fudan University scientists have discovered human brain signals traveling across the outer layer of neural tissue that naturally arrange themselves to resemble swirling spirals.
Scientists discover spiral-shaped signals that organize brain activityUniversity of Sydney and Fudan University scientists have discovered human brain signals traveling across the outer layer of neural tissue that naturally arrange themselves to resemble swirling spirals.
Consulte Mais informação »
 These neurohacking AI headphones can track your brain waves to help you focusCertain headphones will soon be able read your mind
These neurohacking AI headphones can track your brain waves to help you focusCertain headphones will soon be able read your mind
Consulte Mais informação »
 Scientists develop universal donor stem cell therapy to treat degenerative brain diseases in a preclinical studyScientists at City of Hope have developed universal donor stem cells that could one day provide lifesaving therapy to children with lethal brain conditions, such as Canavan disease, as well as to people with other degenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and multiple sclerosis. The study was recently published in Advanced Science.
Scientists develop universal donor stem cell therapy to treat degenerative brain diseases in a preclinical studyScientists at City of Hope have developed universal donor stem cells that could one day provide lifesaving therapy to children with lethal brain conditions, such as Canavan disease, as well as to people with other degenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and multiple sclerosis. The study was recently published in Advanced Science.
Consulte Mais informação »
