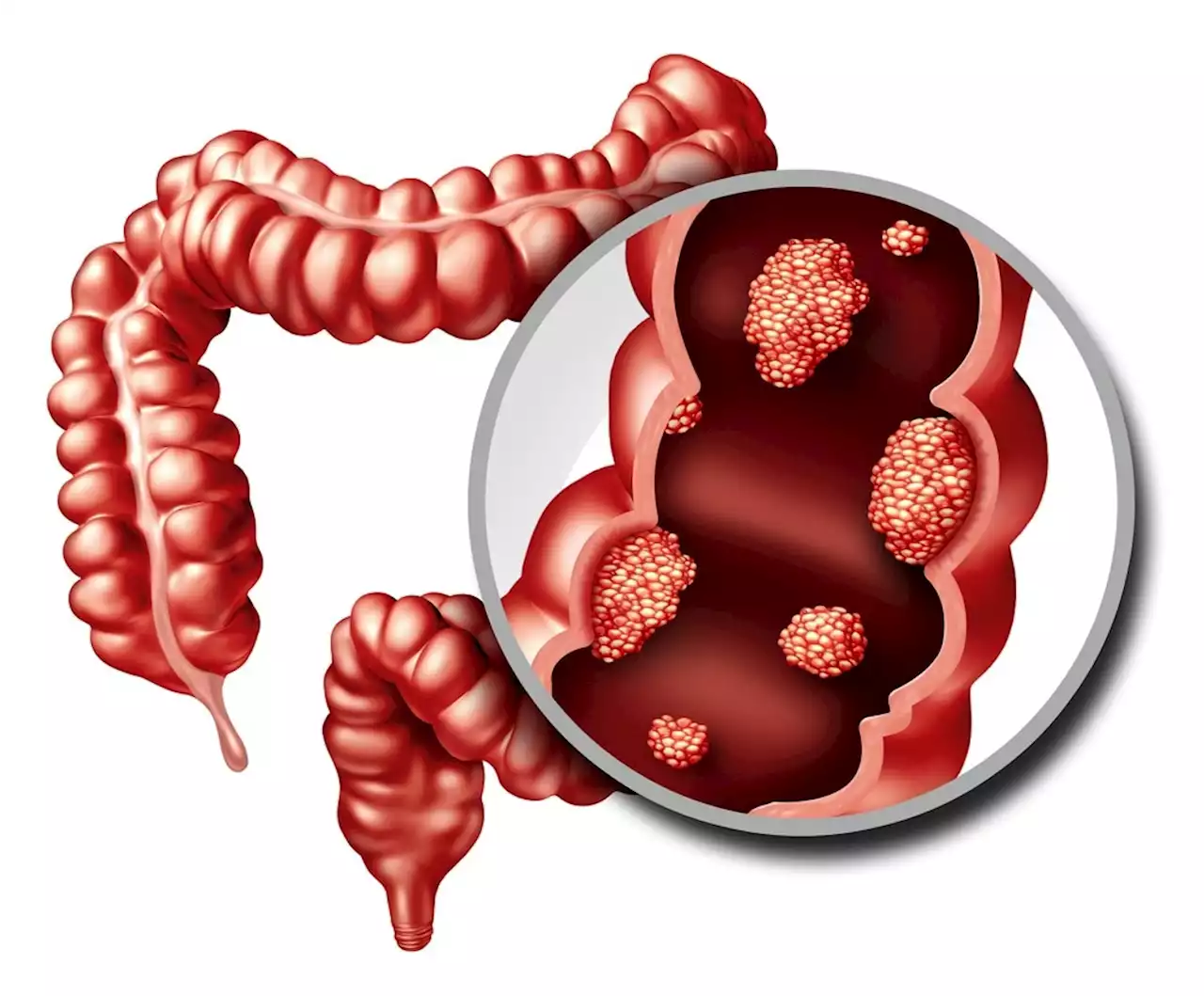
A new trial to assess if butyrate can prevent colon cancer Cancer Butyrate ColonCancer Oncology ELSSurgery CSIRO UniMelb MDAndersonNews UNSW
By Bhavana KunkalikarFeb 16 2023Reviewed by Benedette Cuffari, M.Sc. In a recent study published in the journal Contemporary Clinical Trials Communications, researchers discuss a new clinical trial that will determine the efficacy of butyrate administration in preventing colon cancer.
Despite the advantageous properties of butyrate, excess exposure to butyrate may cause cancer cells to become resistant to its protective effects. After baseline colonoscopy examinations, individuals will be administered either low amylose maize starch or HAMSB for 26-28 weeks, following which a second colonoscopy is performed. The participants will subsequently ingest the alternative starch for 26-28 weeks before undergoing a third colonoscopy after 52 weeks.
Throughout the duration of the trial, the participants, research team, and study coordinators are blinded to the therapies, as well as both the sample and data analysis. The research coordinator uses an electronic case report form to obtain information and allow gastroenterologists from various clinical sites to evaluate the captured videos at the conclusion of the study.
Brasil Últimas Notícias, Brasil Manchetes
Similar News:Você também pode ler notícias semelhantes a esta que coletamos de outras fontes de notícias.
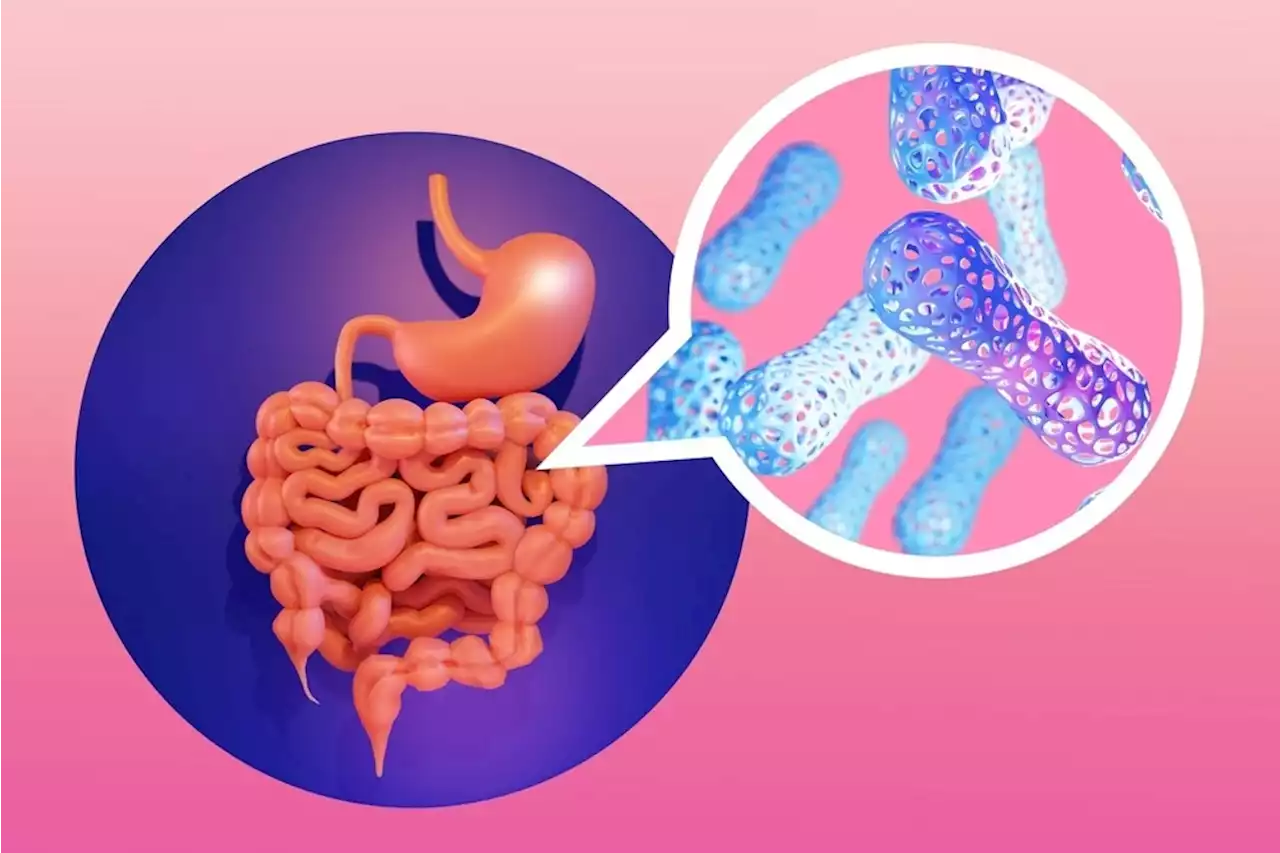 Reduced butyrate production in the microbiome of type 2 diabeticsReduced butyrate production in the microbiome of type 2 diabetics Diabetes Microbiome Type2Diabetes Butyrate TH_Wildau goetheuni
Reduced butyrate production in the microbiome of type 2 diabeticsReduced butyrate production in the microbiome of type 2 diabetics Diabetes Microbiome Type2Diabetes Butyrate TH_Wildau goetheuni
Consulte Mais informação »
 Study on the correlation between B vitamins and breast cancer - Cancer Cell InternationalBackground Relevant studies suggest that serum vitamin level is related to the risk of breast cancer, and dietary pattern and drug supplementation can significantly affect the level of vitamin in the body. Therefore, intervention of vitamin level in the body is expected to be a potential strategy to reduce the risk of breast cancer. However, the current epidemiological findings of serum vitamin levels and breast cancer risk are inconsistent, and the relationship between serum vitamin and breast cancer is still controversial. In this study, we compared the serum vitamin expression levels of healthy people, benign breast patients, and breast cancer patients, and evaluated the relationship between B vitamin levels and breast cancer risk. Methods The study used liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry to determine the serum vitamin levels of 520 people who attended Yunnan Cancer Hospital from September 2020 to December 2020. After screening by exclusion criteria, 38 patients with benign breast diseases, 87 patients with breast cancer and 91 healthy controls were finally included. The kruskal–wallis H test was used to compare the differences in serum vitamin levels of subjects. Χ2 test was used to evaluate the relationship between B vitamin level and age,BMI,TNM staging,Ki-67,Her-2,surgery and chemotherapy, and other baseline characteristics and through binary logistic regression analysis, calculating odds ratio and 95% confidence interval (CI) to evaluate the relationship between B vitamins and breast cancer risk. Conclusion The levels of VitB1 and VitB5 in the serum of breast cancer patients and patients with benign breast diseases were higher than those in the healthy control group, while the expression levels of VitB3 in breast cancer patients were lower than those in the healthy control group and the breast benign disease groups. The level of VitB1 was positively correlated with breast cancer risk. The VitB3 level was negatively correlated with breast cancer r
Study on the correlation between B vitamins and breast cancer - Cancer Cell InternationalBackground Relevant studies suggest that serum vitamin level is related to the risk of breast cancer, and dietary pattern and drug supplementation can significantly affect the level of vitamin in the body. Therefore, intervention of vitamin level in the body is expected to be a potential strategy to reduce the risk of breast cancer. However, the current epidemiological findings of serum vitamin levels and breast cancer risk are inconsistent, and the relationship between serum vitamin and breast cancer is still controversial. In this study, we compared the serum vitamin expression levels of healthy people, benign breast patients, and breast cancer patients, and evaluated the relationship between B vitamin levels and breast cancer risk. Methods The study used liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry to determine the serum vitamin levels of 520 people who attended Yunnan Cancer Hospital from September 2020 to December 2020. After screening by exclusion criteria, 38 patients with benign breast diseases, 87 patients with breast cancer and 91 healthy controls were finally included. The kruskal–wallis H test was used to compare the differences in serum vitamin levels of subjects. Χ2 test was used to evaluate the relationship between B vitamin level and age,BMI,TNM staging,Ki-67,Her-2,surgery and chemotherapy, and other baseline characteristics and through binary logistic regression analysis, calculating odds ratio and 95% confidence interval (CI) to evaluate the relationship between B vitamins and breast cancer risk. Conclusion The levels of VitB1 and VitB5 in the serum of breast cancer patients and patients with benign breast diseases were higher than those in the healthy control group, while the expression levels of VitB3 in breast cancer patients were lower than those in the healthy control group and the breast benign disease groups. The level of VitB1 was positively correlated with breast cancer risk. The VitB3 level was negatively correlated with breast cancer r
Consulte Mais informação »
 Variability Among Breast Cancer Risk Classification Models When Applied at the Level of the Individual Woman - Journal of General Internal MedicineBackground Breast cancer risk models guide screening and chemoprevention decisions, but the extent and effect of variability among models, particularly at the individual level, is uncertain. Objective To quantify the accuracy and disagreement between commonly used risk models in categorizing individual women as average vs. high risk for developing invasive breast cancer. Design Comparison of three risk prediction models: Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool (BCRAT), Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium (BCSC) model, and International Breast Intervention Study (IBIS) model. Subjects Women 40 to 74 years of age presenting for screening mammography at a multisite health system between 2011 and 2015, with 5-year follow-up for cancer outcome. Main Measures Comparison of model discrimination and calibration at the population level and inter-model agreement for 5-year breast cancer risk at the individual level using two cutoffs (≥ 1.67% and ≥ 3.0%). Key Results A total of 31,115 women were included. When using the ≥ 1.67% threshold, more than 21% of women were classified as high risk for developing breast cancer in the next 5 years by one model, but average risk by another model. When using the ≥ 3.0% threshold, more than 5% of women had disagreements in risk severity between models. Almost half of the women (46.6%) were classified as high risk by at least one of the three models (e.g., if all three models were applied) for the threshold of ≥ 1.67%, and 11.1% were classified as high risk for ≥ 3.0%. All three models had similar accuracy at the population level. Conclusions Breast cancer risk estimates for individual women vary substantially, depending on which risk assessment model is used. The choice of cutoff used to define high risk can lead to adverse effects for screening, preventive care, and quality of life for misidentified individuals. Clinicians need to be aware of the high false-positive and false-negative rates and variation between models when talking with pati
Variability Among Breast Cancer Risk Classification Models When Applied at the Level of the Individual Woman - Journal of General Internal MedicineBackground Breast cancer risk models guide screening and chemoprevention decisions, but the extent and effect of variability among models, particularly at the individual level, is uncertain. Objective To quantify the accuracy and disagreement between commonly used risk models in categorizing individual women as average vs. high risk for developing invasive breast cancer. Design Comparison of three risk prediction models: Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool (BCRAT), Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium (BCSC) model, and International Breast Intervention Study (IBIS) model. Subjects Women 40 to 74 years of age presenting for screening mammography at a multisite health system between 2011 and 2015, with 5-year follow-up for cancer outcome. Main Measures Comparison of model discrimination and calibration at the population level and inter-model agreement for 5-year breast cancer risk at the individual level using two cutoffs (≥ 1.67% and ≥ 3.0%). Key Results A total of 31,115 women were included. When using the ≥ 1.67% threshold, more than 21% of women were classified as high risk for developing breast cancer in the next 5 years by one model, but average risk by another model. When using the ≥ 3.0% threshold, more than 5% of women had disagreements in risk severity between models. Almost half of the women (46.6%) were classified as high risk by at least one of the three models (e.g., if all three models were applied) for the threshold of ≥ 1.67%, and 11.1% were classified as high risk for ≥ 3.0%. All three models had similar accuracy at the population level. Conclusions Breast cancer risk estimates for individual women vary substantially, depending on which risk assessment model is used. The choice of cutoff used to define high risk can lead to adverse effects for screening, preventive care, and quality of life for misidentified individuals. Clinicians need to be aware of the high false-positive and false-negative rates and variation between models when talking with pati
Consulte Mais informação »
 Largest ever Yorkshire dinosaur print 'left by lazing giant,' researchers sayResearchers publish findings on an 'amazing' dinosaur print found on Yorkshire's coast.
Largest ever Yorkshire dinosaur print 'left by lazing giant,' researchers sayResearchers publish findings on an 'amazing' dinosaur print found on Yorkshire's coast.
Consulte Mais informação »
 Largest ever Yorkshire dinosaur print 'left by lazing giant,' researchers sayResearchers publish findings on an 'amazing' dinosaur print found on Yorkshire's coast.
Largest ever Yorkshire dinosaur print 'left by lazing giant,' researchers sayResearchers publish findings on an 'amazing' dinosaur print found on Yorkshire's coast.
Consulte Mais informação »
 New insights into the role of T-cells during long COVIDNew insights into the role of T-cells during long COVID Coronavirus Disease COVID TCell biorxivpreprint UCSF uni_ulm
New insights into the role of T-cells during long COVIDNew insights into the role of T-cells during long COVID Coronavirus Disease COVID TCell biorxivpreprint UCSF uni_ulm
Consulte Mais informação »